Ectopic application of the repressive histone modification H3K9me2 establishes post-zygotic reproductive isolation in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 28743695
- PMCID: PMC5558928
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.299347.117
Ectopic application of the repressive histone modification H3K9me2 establishes post-zygotic reproductive isolation in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
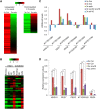
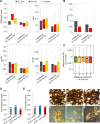
Hybrid seed lethality as a consequence of interspecies or interploidy hybridizations is a major mechanism of reproductive isolation in plants. This mechanism is manifested in the endosperm, a dosage-sensitive tissue supporting embryo growth. Deregulated expression of imprinted genes such as ADMETOS (ADM) underpin the interploidy hybridization barrier in Arabidopsis thaliana; however, the mechanisms of their action remained unknown. In this study, we show that ADM interacts with the AT hook domain protein AHL10 and the SET domain-containing SU(VAR)3-9 homolog SUVH9 and ectopically recruits the heterochromatic mark H3K9me2 to AT-rich transposable elements (TEs), causing deregulated expression of neighboring genes. Several hybrid incompatibility genes identified in Drosophila encode for dosage-sensitive heterochromatin-interacting proteins, which has led to the suggestion that hybrid incompatibilities evolve as a consequence of interspecies divergence of selfish DNA elements and their regulation. Our data show that imbalance of dosage-sensitive chromatin regulators underpins the barrier to interploidy hybridization in Arabidopsis, suggesting that reproductive isolation as a consequence of epigenetic regulation of TEs is a conserved feature in animals and plants.
Keywords: endosperm; heterochromatin; hybrid incompatibility; imprinted genes; polyploidy; transposable elements.
© 2017 Jiang et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An imprinted gene underlies postzygotic reproductive isolation in Arabidopsis thaliana.Dev Cell. 2013 Sep 16;26(5):525-35. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.08.006. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Dev Cell. 2013. PMID: 24012484
-
Mutants in the imprinted PICKLE RELATED 2 gene suppress seed abortion of fertilization independent seed class mutants and paternal excess interploidy crosses in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2017 Apr;90(2):383-395. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13500. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 28155248
-
Hypomethylated pollen bypasses the interploidy hybridization barrier in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2014 Sep;26(9):3556-68. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.130120. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 25217506 Free PMC article.
-
SET domain proteins in plant development.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Aug;1809(8):407-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.05.008. Epub 2011 May 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21664308 Review.
-
Tearing down barriers: understanding the molecular mechanisms of interploidy hybridizations.J Exp Bot. 2012 Oct;63(17):6059-67. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers288. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 23105129 Review.
Cited by
-
The MADS-box transcription factor PHERES1 controls imprinting in the endosperm by binding to domesticated transposons.Elife. 2019 Dec 2;8:e50541. doi: 10.7554/eLife.50541. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31789592 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis and evolutionary drivers of endosperm-based hybridization barriers.Plant Physiol. 2024 Apr 30;195(1):155-169. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiae050. Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38298124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of cytokinin receptors in Arabidopsis thaliana seed development and how they affect the metabolomic profile.Planta. 2025 Jul 18;262(3):59. doi: 10.1007/s00425-025-04745-7. Planta. 2025. PMID: 40679558
-
Mutation of histone H3 serine 28 to alanine influences H3K27me3-mediated gene silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Physiol. 2022 Nov 28;190(4):2417-2429. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac409. Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36053193 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic and transcriptional consequences in the endosperm of chemically induced transposon mobilization in Arabidopsis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 27;52(15):8833-8848. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae572. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38967011 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birchler JA, Bhadra U, Bhadra MP, Auger DL. 2001. Dosage-dependent gene regulation in multicellular eukaryotes: implications for dosage compensation, aneuploid syndromes, and quantitative traits. Dev Biol 234: 275–288. - PubMed
-
- Blumenstiel JP. 2011. Evolutionary dynamics of transposable elements in a small RNA world. Trends Genet 27: 23–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
