Disease-causing mutations in the serpin antithrombin reveal a key domain critical for inhibiting protease activities
- PMID: 28743742
- PMCID: PMC5633112
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.787325
Disease-causing mutations in the serpin antithrombin reveal a key domain critical for inhibiting protease activities
Abstract
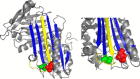
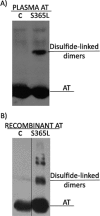
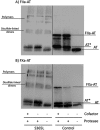
Antithrombin mainly inhibits factor Xa and thrombin. The reactive center loop (RCL) is crucial for its interactions with its protease targets and is fully inserted into the A-sheet after its cleavage, causing translocation of the covalently linked protease to the opposite end of the A-sheet. Antithrombin variants with altered RCL hinge residues behave as substrates rather than inhibitors, resulting in stoichiometries of inhibition greater than one. Other antithrombin residues have been suggested to interfere with RCL insertion or the stability of the antithrombin-protease complex, but available crystal structures or mutagenesis studies have failed to identify such residues. Here, we characterized two mutations, S365L and I207T, present in individuals with type II antithrombin deficiency and identified a new antithrombin functional domain. S365L did not form stable complexes with thrombin or factor Xa, and the I207T/I207A variants inhibited both proteases with elevated stoichiometries of inhibition. Close proximity of Ile-207 and Ser-365 to the inserted RCL suggested that the preferred reaction of these mutants as protease substrates reflects an effect on the rate of the RCL insertion and protease translocation. However, both residues lie within the final docking site for the protease in the antithrombin-protease complex, supporting the idea that the enhanced substrate reactions may result from an increased dissociation of the final complexes. Our findings demonstrate that the distal end of the antithrombin A-sheet is crucial for the last steps of protease inhibition either by affecting the rate of RCL insertion or through critical interactions with proteases at the end of the A-sheet.
Keywords: antithrombin (AT); complex; factor Xa; inhibition; inhibition mechanism; kinetics; stoichiometry; thrombin.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Comment in
-
A novel antithrombin domain dictates the journey's end of a proteinase.J Biol Chem. 2017 Oct 6;292(40):16521-16522. doi: 10.1074/jbc.H117.787325. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28986431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gils A., and Declerck P. J. (1998) Structure-function relationships in serpins: current concepts and controversies. Thromb. Haemost. 80, 531–541 - PubMed
-
- Olson S. T., Richard B., Izaguirre G., Schedin-Weiss S., and Gettins P. G. W. (2010) Molecular mechanisms of antithrombin-heparin regulation of blood clotting proteinases: a paradigm for understanding proteinase regulation by serpin family protein proteinase inhibitors. Biochimie 92, 1587–1596 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Olson S. T., Björk I., Sheffer R., Craig P. A., Shore J. D., and Choay J. (1992) Role of the antithrombin-binding pentasaccharide in heparin acceleration of antithrombin-proteinase reactions: resolution of the antithrombin conformational change contribution to heparin rate enhancement. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 12528–12538 - PubMed
-
- Izaguirre G., and Olson S. T. (2006) Residues Tyr253 and Glu255 in strand 3 of β-sheet C of antithrombin are key determinants of an exosite made accessible by heparin activation to promote rapid inhibition of factors Xa and IXa. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 13424–13432 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

