Spotlight on brodalumab in the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: design, development, and potential place in therapy
- PMID: 28744098
- PMCID: PMC5511025
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S113683
Spotlight on brodalumab in the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: design, development, and potential place in therapy
Abstract
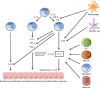
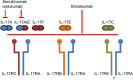
Brodalumab is a novel fully human immunoglobulin G2 monoclonal antibody that antagonizes the interleukin (IL)-17 pathway by binding with high affinity to human IL-17RA. The role of IL-17A in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, as well as the remarkable effectiveness of IL-17 inhibitors in the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, is well established. The mechanism of action of brodalumab is unique in that it inhibits the IL-17 receptor compared to the two other currently FDA-approved IL-17 inhibitors, secukinumab and ixekizumab, which inhibit the IL-17A molecule itself. The efficacy of brodalumab in the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis has been demonstrated in phase 2 and 3 trials, and subsequently the FDA approved this medication in February 2017. Brodalumab was approved in Japan in July 2016 and approval is pending in Europe. The safety and adverse effects of brodalumab were reviewed across several clinical trials, which, similar to other IL-17 inhibitors, demonstrated increased rates of neutropenia and Candida infections. Brodalumab treatment, similar to ixekizumab and secukinumab, showed no improvement in inflammatory bowel disease patients, and on the contrary, more exacerbations were encountered. Suicidal ideation and behavior events have been reported with brodalumab treatment and are of significant concern. Brodalumab provides another highly effective treatment option for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.
Keywords: IL-17; biologics; brodalumab; plaque psoriasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brodalumab: the first anti-IL-17 receptor agent for psoriasis.Drugs Today (Barc). 2017 May;53(5):283-297. doi: 10.1358/dot.2017.53.5.2613690. Drugs Today (Barc). 2017. PMID: 28650001 Review.
-
Anti-interleukin-17 treatment of psoriasis.J Dermatolog Treat. 2016 Aug;27(4):311-5. doi: 10.3109/09546634.2015.1115816. Epub 2016 Mar 4. J Dermatolog Treat. 2016. PMID: 26943806 Review.
-
Brodalumab for the treatment of psoriasis.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016 Dec;12(12):1255-1271. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2016.1246957. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27718760 Review.
-
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitors in the treatment of plaque psoriasis: a review.Skin Therapy Lett. 2015 Jan-Feb;20(1):1-5. Skin Therapy Lett. 2015. PMID: 25807214 Review.
-
Anti-IL17 therapies for psoriasis.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019 Jan;19(1):45-54. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2019.1555235. Epub 2018 Dec 8. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30500317 Review.
Cited by
-
Brodalumab for Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review of Efficacy, Safety, and Clinical Positioning.Biologics. 2025 Jul 15;19:415-422. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S532526. eCollection 2025. Biologics. 2025. PMID: 40688593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Brodalumab on the Fungal Microbiome in Patients with Psoriasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 24;25(19):10239. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910239. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408568 Free PMC article.
-
Malignancy Rates in Brodalumab Clinical Studies for Psoriasis.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020 Jun;21(3):421-430. doi: 10.1007/s40257-020-00512-4. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32207067 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Interleukin 23/17 Axis in Psoriasis Management: A Comprehensive Review of Clinical Trials.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024 Apr 10;17:829-842. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S462797. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38616886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-17 and Interleukin-23: A Narrative Review of Mechanisms of Action in Psoriasis and Associated Comorbidities.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021 Apr;11(2):385-400. doi: 10.1007/s13555-021-00483-2. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021. PMID: 33512665 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gelfand JM, Weinstein R, Porter SB, Neimann AL, Berlin JA, Margolis DJ. Prevalence and treatment of psoriasis in the United Kingdom: a population-based study. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141(12):1537–1541. - PubMed
-
- Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70(3):512–516. - PubMed
-
- Augustin M, Radtke MA. Quality of life in psoriasis patients. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2014;14(4):559–568. - PubMed
-
- Abuhilal M, Walsh S, Shear N. The role of IL-17 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and update on IL-17 inhibitors for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20(6):509–516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

