All-Atom MD Predicts Magnesium-Induced Hairpin in Chemically Perturbed RNA Analog of F10 Therapeutic
- PMID: 28745046
- PMCID: PMC5719488
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b04724
All-Atom MD Predicts Magnesium-Induced Hairpin in Chemically Perturbed RNA Analog of F10 Therapeutic
Abstract
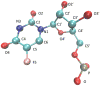
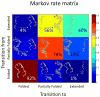
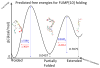
Given their increasingly frequent usage, understanding the chemical and structural properties which allow therapeutic nucleic acids to promote the death of cancer cells is critical for medical advancement. One molecule of interest is a 10-mer of FdUMP (5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine-5'-O-monophosphate) also called F10. To investigate causes of structural stability, we have computationally restored the 2' oxygen on each ribose sugar of the phosphodiester backbone, creating FUMP[10]. Microsecond time-scale, all-atom, simulations of FUMP[10] in the presence of 150 mM MgCl2 predict that the strand has a 45% probability of folding into a stable hairpin-like secondary structure. Analysis of 16 μs of data reveals phosphate interactions as likely contributors to the stability of this folded state. Comparison with polydT and polyU simulations predicts that FUMP[10]'s lowest order structures last for one to 2 orders of magnitude longer than similar nucleic acid strands. Here we provide a brief structural and conformational analysis of the predicted structures of FUMP[10], and suggest insights into its stability via comparison to F10, polydT, and polyU.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Dr. Gmeiner is an owner of Salzburg Therapeutics, the company holding licenses for FdUMP-[N].
Figures
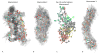



Similar articles
-
All-Atom Molecular Dynamics Reveals Mechanism of Zinc Complexation with Therapeutic F10.J Phys Chem B. 2016 Oct 6;120(39):10269-10279. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b07753. Epub 2016 Sep 21. J Phys Chem B. 2016. PMID: 27606431 Free PMC article.
-
All-atom MD indicates ion-dependent behavior of therapeutic DNA polymer.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017 Aug 23;19(33):22363-22374. doi: 10.1039/c7cp03479b. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017. PMID: 28805211 Free PMC article.
-
Structures, dynamics, and stabilities of fully modified locked nucleic acid (β-D-LNA and α-L-LNA) duplexes in comparison to pure DNA and RNA duplexes.J Phys Chem B. 2013 May 9;117(18):5556-64. doi: 10.1021/jp4016068. Epub 2013 Apr 25. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 23617391
-
Structure-editing of nucleic acids for selective targeting of RNA.Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(7):715-26. doi: 10.2174/156802607780487722. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17430211 Review.
-
On using magnesium and potassium ions in RNA experiments.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1206:157-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1369-5_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25240895 Review.
Cited by
-
Allosteric Modulation of Thrombin by Thrombomodulin: Insights from Logistic Regression and Statistical Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Simulations.ACS Omega. 2024 May 17;9(21):23086-23100. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c03375. eCollection 2024 May 28. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38826540 Free PMC article.
-
Using correlated motions to determine sufficient sampling times for molecular dynamics.Phys Rev E. 2018 Aug;98(2-1):023307. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.98.023307. Phys Rev E. 2018. PMID: 30253618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skutella T, Stöhr T, Probst JC, Ramalho-Ortigao FJ, Holsboer F, Jirikowski GF. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides for in vivo targeting of corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA: comparison of phosphorothioate and 3′-inverted probe performance. Horm Metab Res. 1994;26:460–464. - PubMed
-
- Souza P, Sedlackova L, Kuliszewski M, Wang J, Liu J, Tseu I, Liu M, Tanswell AK, Post M. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides targeting PDGF-B mRNA inhibit cell proliferation during embryonic rat lung development. Development. 1994;120:2163–2173. - PubMed
-
- Konopka K, Rossi JJ, Swiderski P, Slepushkin Va, Düzgüneş N. Delivery of an anti-HIV-1 ribozyme into HIV-infected cells via cationic liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta, Biomembr. 1998;1372:55–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

