The androgen receptor is a negative regulator of eIF4E phosphorylation at S209: implications for the use of mTOR inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer
- PMID: 28745319
- PMCID: PMC5690844
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2017.233
The androgen receptor is a negative regulator of eIF4E phosphorylation at S209: implications for the use of mTOR inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer
Abstract
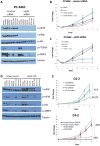
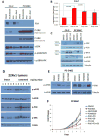
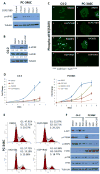
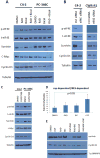
The antiandrogen bicalutamide is widely used in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer (PCa) in many countries, but its effect on castration-resistant PCa (CRPC) is limited. We previously showed that resistance to bicalutamide results from activation of mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR). Interestingly, clinical trials testing combinations of the mTOR inhibitor RAD001 with bicalutamide were effective in bicalutamide-naïve CRPC patients, but not in bicalutamide-pretreated ones. Here we investigate causes for their difference in response. Evaluation of CRPC cell lines identified resistant vs sensitive in vitro models, and revealed that increased eIF4E(S209) phosphorylation is associated with resistance to the combination. We confirmed using a human-derived tumor xenograft mouse model that bicalutamide pre-treatment is associated with an increase in eIF4E(S209) phosphorylation. Thus, AR suppressed eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) phosphorylation, while the use of antiandrogens relieved this suppression, thereby triggering its increase. Additional investigation in human prostatectomy samples showed that increased eIF4E phosphorylation strongly correlated with the cell proliferation marker Ki67. Small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown (k/d) of eIF4E-sensitized CRPC cells to RAD001+bicalutamide, whereas eIF4E overexpression induced resistance. Inhibition of eIF4E phosphorylation by treatment with CGP57380 (an inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase-interacting serine-threonine kinases MAP kinase-interacting kinase 1 (Mnk1/2), the eIF4E upstream kinase) or inhibitors of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), the upstream kinase-regulating Mnk1/2, also sensitized CRPC cells to RAD001+bicalutamide. Examination of downstream targets of eIF4E-mediated translation, including survivin, demonstrated that eIF4E(S209) phosphorylation increased cap-independent translation, whereas its inhibition restored cap-dependent translation, which could be inhibited by mTOR inhibitors. Thus, our results demonstrate that while combinations of AR and mTOR inhibitors were effective in suppressing tumor growth by inhibiting both AR-induced transcription and mTOR-induced cap-dependent translation, pre-treatment with AR antagonists including bicalutamide increased eIF4E phosphorylation that induced resistance to combinations of AR and mTOR inhibitors by inducing cap-independent translation. We conclude that this resistance can be overcome by inhibiting eIF4E phosphorylation with Mnk1/2 or ERK1/2 inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The work reported here does not represent the views or opinions of the Department of Veteran Affairs or the United States Government.
Figures
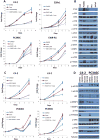
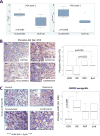
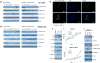
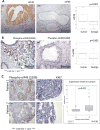
Similar articles
-
eIF4E Phosphorylation in Prostate Cancer.Neoplasia. 2018 Jun;20(6):563-573. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 May 4. Neoplasia. 2018. PMID: 29730477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CGP57380 enhances efficacy of RAD001 in non-small cell lung cancer through abrogating mTOR inhibition-induced phosphorylation of eIF4E and activating mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):27787-801. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8497. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27050281 Free PMC article.
-
MNK1 inhibitor CGP57380 overcomes mTOR inhibitor-induced activation of eIF4E: the mechanism of synergic killing of human T-ALL cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Dec;39(12):1894-1901. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0161-0. Epub 2018 Oct 8. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 30297804 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin induces phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent and Mnk-mediated eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E phosphorylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Nov;27(21):7405-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00760-07. Epub 2007 Aug 27. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17724079 Free PMC article.
-
Dual targeting of eIF4E by blocking MNK and mTOR pathways in leukemia.Cytokine. 2017 Jan;89:116-121. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.01.024. Epub 2016 Apr 16. Cytokine. 2017. PMID: 27094611 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Galeterone and The Next Generation Galeterone Analogs, VNPP414 and VNPP433-3β Exert Potent Therapeutic Effects in Castration-/Drug-Resistant Prostate Cancer Preclinical Models In Vitro and In Vivo.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 24;11(11):1637. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111637. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31653008 Free PMC article.
-
eIF4E Phosphorylation in Prostate Cancer.Neoplasia. 2018 Jun;20(6):563-573. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 May 4. Neoplasia. 2018. PMID: 29730477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MAP Kinase-Interacting Kinase 1 Promotes Proliferation and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Is an Unfavorable Prognostic Biomarker.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Mar 26;24:1759-1767. doi: 10.12659/msm.909012. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29576605 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and Molecular Progression of Prostate Cancer: Models for Basic and Preclinical Research.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 17;12(9):2651. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092651. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32957478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Natural Compound Homoharringtonine Presents Broad Antiviral Activity In Vitro and In Vivo.Viruses. 2018 Nov 1;10(11):601. doi: 10.3390/v10110601. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30388805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- MacVicar GR, Hussain MH. Emerging therapies in metastatic castration-sensitive and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013;25(3):252–60. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh PM, Malik SN, Bedolla RG, Wang Y, Mikhailova M, Prihoda TJ, et al. Signal transduction pathways in androgen-dependent and -independent prostate cancer cell proliferation. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12(1):119–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

