Precannulated Fenestrated Endovascular Aneurysm Repair Using Guidewire Fixator: A Novel Method Using the Liungman Guidewire Fixator
- PMID: 28746064
- PMCID: PMC5559182
- DOI: 10.1097/IMI.0000000000000392
Precannulated Fenestrated Endovascular Aneurysm Repair Using Guidewire Fixator: A Novel Method Using the Liungman Guidewire Fixator
Abstract
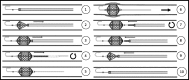
Objective: By using a guidewire fixator, the distal guidewire position can be secured in an artery. This new principle enables a method for fenestrated endovascular aortic repair where the connection between the aortic branches and the stent graft fenestrations is made before inserting and deploying the stent graft.
Methods: This is conducted using a fenestrated stent graft with preloaded catheters, through which the prepositioned and distally secured guidewires from the branches are inserted.
Results: This report covers the method when implementing a single fenestration stent graft in pig.
Conclusions: Successful tests with single and dual fenestrated grafts have been conducted in pigs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Safety and Functionality of a Guidewire Fixator: Clinical Investigation of a New Endovascular Tool.Innovations (Phila). 2018 Jan/Feb;13(1):51-53. doi: 10.1097/IMI.0000000000000468. Innovations (Phila). 2018. PMID: 29465630 Free PMC article.
-
Fenestrated TEVAR Using a Guidewire Fixator for Anchoring in Aortic Arch Target Vessels.J Endovasc Ther. 2018 Feb;25(1):40-46. doi: 10.1177/1526602817744344. Epub 2017 Nov 29. J Endovasc Ther. 2018. PMID: 29187014
-
Electromagnetically Navigated In Situ Fenestration of Aortic Stent Grafts: Pilot Animal Study of a Novel Fenestrated EVAR Approach.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018 Jan;41(1):170-176. doi: 10.1007/s00270-017-1769-z. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018. PMID: 28821949
-
Fenestrated and branched endovascular techniques for thoraco-abdominal aneurysm repair.J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2005 Apr;46(2):131-40. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2005. PMID: 15793492 Review.
-
Endovascular aortic aneurysm repair with chimney and snorkel grafts: indications, techniques and results.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013 Dec;36(6):1443-1451. doi: 10.1007/s00270-013-0648-5. Epub 2013 May 15. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23674274 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety and Functionality of a Guidewire Fixator: Clinical Investigation of a New Endovascular Tool.Innovations (Phila). 2018 Jan/Feb;13(1):51-53. doi: 10.1097/IMI.0000000000000468. Innovations (Phila). 2018. PMID: 29465630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenberg RK, Sternbergh WC, III, Makaroun M, et al. Intermediate results of a United States multicenter trial of fenestrated endograft repair for juxtarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2009;50:730–737. - PubMed
-
- Amiot S, Haulon S, Becquemin JP, et al. Fenestrated endovascular grafting: the French multicentre experience. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010;39:537–544. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

