CD73 expression identifies a subset of IgM+ antigen-experienced cells with memory attributes that is T cell and CD40 signalling dependent
- PMID: 28746783
- PMCID: PMC5680063
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12800
CD73 expression identifies a subset of IgM+ antigen-experienced cells with memory attributes that is T cell and CD40 signalling dependent
Abstract
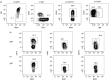
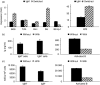
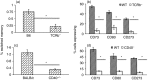
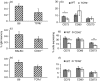
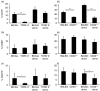
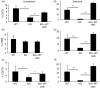
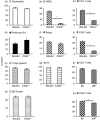
B-cell memory was long characterized as isotype-switched, somatically mutated and germinal centre (GC)-derived. However, it is now clear that the memory pool is a complex mixture that includes unswitched and unmutated cells. Further, expression of CD73, CD80 and CD273 has allowed the categorization of B-cell memory into multiple subsets, with combinatorial expression of the markers increasing with GC progression, isotype-switching and acquisition of somatic mutations. We have extended these findings to determine whether these markers can be used to identify IgM memory phenotypically as arising from T-dependent versus T-independent responses. We report that CD73 expression identifies a subset of antigen-experienced IgM+ cells that share attributes of functional B-cell memory. This subset is reduced in the spleens of T-cell-deficient and CD40-deficient mice and in mixed marrow chimeras made with mutant and wild-type marrow, the proportion of CD73+ IgM memory is restored in the T-cell-deficient donor compartment but not in the CD40-deficient donor compartment, indicating that CD40 ligation is involved in its generation. We also report that CD40 signalling supports optimal expression of CD73 on splenic T cells and age-associated B cells (ABCs), but not on other immune cells such as neutrophils, marginal zone B cells, peritoneal cavity B-1 B cells and regulatory T and B cells. Our data indicate that in addition to promoting GC-associated memory generation during B-cell differentiation, CD40-signalling can influence the composition of the unswitched memory B-cell pool. They also raise the possibility that a fraction of ABCs may represent T-cell-dependent IgM memory.
Keywords: CD40; CD73; IgM; T cells; age-associated B cells; memory.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Slifka MK, Ahmed R. Long‐lived plasma cells: a mechanism for maintaining persistent antibody production. Curr Opin Immunol 1998; 10:252–8. - PubMed
-
- McHeyzer‐Williams MG, Ahmed R. B cell memory and the long‐lived plasma cell. Curr Opin Immunol 1999; 11:172–9. - PubMed
-
- Nutt SL, Hodgkin PD, Tarlinton DM, Corcoran LM. The generation of antibody‐secreting plasma cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2015; 15:160–71. - PubMed
-
- Ho F, Lortan JE, MacLennan IC, Khan M. Distinct short‐lived and long‐lived antibody‐producing cell populations. Eur J Immunol 1986; 16:1297–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

