Natural Conformational Sampling of Human TNFα Visualized by Double Electron-Electron Resonance
- PMID: 28746848
- PMCID: PMC5529296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.06.007
Natural Conformational Sampling of Human TNFα Visualized by Double Electron-Electron Resonance
Abstract
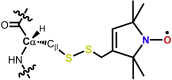
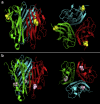
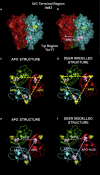
Double electron-electron resonance in conjunction with site-directed spin labeling has been used to probe natural conformational sampling of the human tumor necrosis factor α trimer. We suggest a previously unreported, predeoligomerization conformation of the trimer that has been shown to be sampled at low frequency. A model of this trimeric state has been constructed based on crystal structures using the double-electron-electron-resonance distances. The model shows one of the protomers to be rotated and tilted outward at the tip end, leading to a breaking of the trimerous symmetry and distortion at a receptor-binding interface. The new structure offers opportunities to modulate the biological activity of tumor necrosis factor α through stabilization of the distorted trimer with small molecules.
Copyright © 2017 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

