Thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1), a new bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -4 (BMP-2/4) antagonist identified in pituitary cells
- PMID: 28747434
- PMCID: PMC5602395
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.736207
Thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1), a new bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -4 (BMP-2/4) antagonist identified in pituitary cells
Abstract
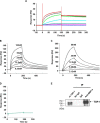
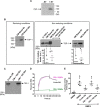
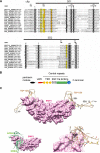
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) regulate diverse cellular responses during embryogenesis and in adulthood including cell differentiation, proliferation, and death in various tissues. In the adult pituitary, BMPs participate in the control of hormone secretion and cell proliferation, suggesting a potential endocrine/paracrine role for BMPs, but some of the mechanisms are unclear. Here, using a bioactivity test based on embryonic cells (C3H10T1/2) transfected with a BMP-responsive element, we sought to determine whether pituitary cells secrete BMPs or BMP antagonists. Interestingly, we found that pituitary-conditioned medium contains a factor that inhibits action of BMP-2 and -4. Combining surface plasmon resonance and high-resolution mass spectrometry helped pinpoint this factor as thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1). Surface plasmon resonance and co-immunoprecipitation confirmed that recombinant human TSP-1 can bind BMP-2 and -4 and antagonize their effects on C3H10T1/2 cells. Moreover, TSP-1 inhibited the action of serum BMPs. We also report that the von Willebrand type C domain of TSP-1 is likely responsible for this BMP-2/4-binding activity, an assertion based on sequence similarity that TSP-1 shares with the von Willebrand type C domain of Crossveinless 2 (CV-2), a BMP antagonist and member of the chordin family. In summary, we identified for the first time TSP-1 as a BMP-2/-4 antagonist and presented a structural basis for the physical interaction between TSP-1 and BMP-4. We propose that TSP-1 could regulate bioavailability of BMPs, either produced locally or reaching the pituitary via blood circulation. In conclusion, our findings provide new insights into the involvement of TSP-1 in the BMP-2/-4 mechanisms of action.
Keywords: C3H10T1/2 cells; bone morphogenetic protein (BMP); bone morphogenetic protein antagonist; pituitary gland; structural model; surface plasmon resonance (SPR); thrombospondin.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures




References
-
- Wozney J. M., Rosen V., Celeste A. J., Mitsock L. M., Whitters M. J., Kriz R. W., Hewick R. M., and Wang E. A. (1988) Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science 242, 1528–1534 - PubMed
-
- Chen D., Zhao M., and Mundy G. R. (2004) Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors. 22, 233–241 - PubMed
-
- Otsuka F. (2010) Multiple endocrine regulation by bone morphogenetic protein system. Endocr. J. 57, 3–14 - PubMed
-
- Otsuka F. (2013) Multifunctional bone morphogenetic protein system in endocrinology. Acta Med. Okayama. 67, 75–86 - PubMed
-
- Paez-Pereda M., Giacomini D., Refojo D., Nagashima A. C., Hopfner U., Grubler Y., Chervin A., Goldberg V., Goya R., Hentges S. T., Low M. J., Holsboer F., Stalla G. K., and Arzt E. (2003) Involvement of bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP-4) in pituitary prolactinoma pathogenesis through a SMAD/estrogen receptor crosstalk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 1034–1039 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

