Posttravmatik frontoetmoidal mukopiyosel
- PMID: 28747844
- PMCID: PMC5509122
- DOI: 10.5152/TurkPediatriArs.2017.2602
Posttravmatik frontoetmoidal mukopiyosel
Abstract
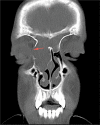
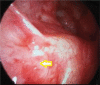
Paranasal sinus mucoceles are mucus-containing cystic structures with an epithelial lining that completely fills in the paranasal sinuses. Although they are benign in nature, they may result in the destruction of the surrounding bony structures over time. Clinical findings such as exophthalmia, visual impairment, and diplopia occur due to pressure of the fronto-ethmoidal mucocele on the orbita. Currently, the endoscopic intranasal approach is preferred in the treatment of paranasal sinus mucoceles due to its minimal morbidity and low recurrence rates. Here, we present a patient aged 12 years who had a right fronto-ethmoidal mucopyocele secondary to a probable trauma 2 years prior, which resulted in proptosis due to pressure on the orbita.
Keywords: Mucopyocele; pediatric; posttraumatic.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Arrue P, Kany MT, Serrano E, et al. Mucoceles of the paranasal sinuses: uncomon location. J Laryngol Otol. 1998;112:840–4. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215100141854. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tinoco P, Pereira JC, Lourenço Filho RC, et al. Tratamento nasoendoscópico da mucocele de seio esfenoidal. Arq Int Otorrinolaringol. 2009;13:336–9.
-
- Nicollas R, Facon F, Sudre-Levillain I, et al. Pediatric paranasal sinus mucoceles: etiologic factors, management and outcome. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006;70:905–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2005.10.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Neuenschwander MC, Pribitkin E, Lacombe V, Maus M, Rao V, Roth M. Frontoethmoid mucocele complicating Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1998;107:433–5. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949810700513. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Conboy PJ, Jones NS. The place of endoscopic sinus surgery in the treatment of paranasal sinus mucoceles. Clin Otolaryngol. 2003;28:207–10. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2273.2003.00690.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

