Role of ghrelin in the pancreatic exocrine secretion via mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in rats
- PMID: 28748103
- PMCID: PMC5523148
- DOI: 10.1186/s40781-017-0141-9
Role of ghrelin in the pancreatic exocrine secretion via mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in rats
Abstract
Background: This study was performed to investigate the impact of exogenous ghrelin on the pancreatic α-amylase outputs and responses of pancreatic proteins to ghrelin that may relate to pancreatic exocrine.
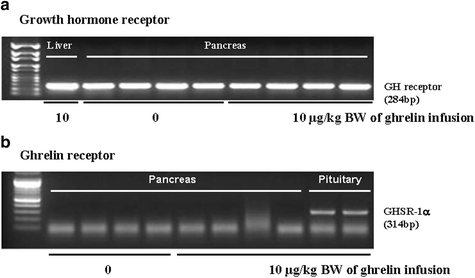
Methods: Sprague-Dawley male rats (9 weeks old, 300 ± 10 g) were injected with ghrelin via intraperitoneal (i.p.) infusion at dosage of 0, 0.1, 1.0 and 10.0 μg/kg body weight (BW), respectively. The plasma ghrelin and cholecystokinin (CCK) level were determined using enzyme immunoassay kit; the mRNA expression of ghrelin receptor (GHSR-1α) and growth hormone (GH) receptor were assessed by reverse transcription PCR; the expressions of pancreatic α-amylase activity, extracellular-signal-regulated kinases (ERK), phosphorylated extracellular-signal-regulated kinases (pERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) were evaluated by western blotting; moreover the responses of pancreatic proteins to ghrelin were analyzed using the two-dimensional gel electrophoresis system.
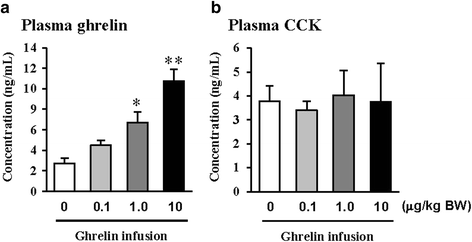
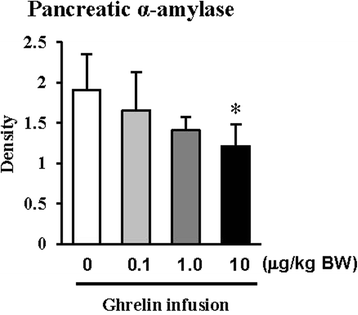
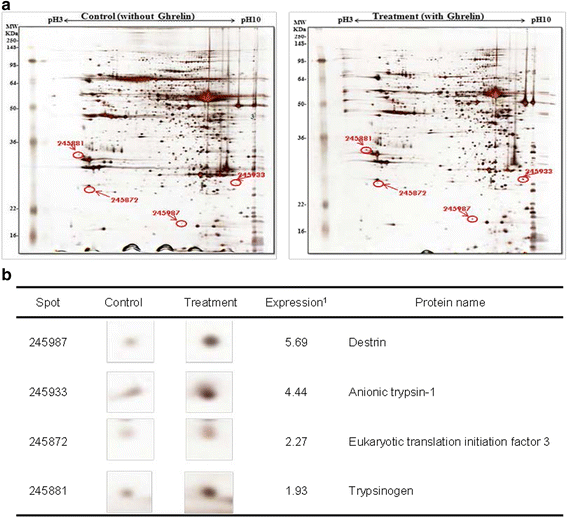
Results: The exogenous ghrelin (1.0 and 10.0 μg/kg BW) elevated the level of plasma ghrelin (p < 0.05), and suppressed the expression of pancreatic α-amylase at a dose of 10.0 μg/kg BW (p < 0.05). No difference in the level of plasma CCK was observed, even though rats were exposed to any dose of exogenous ghrelin. In addition, a combination of western blot and proteomic analysis revealed exogenous ghrelin (10.0 μg/kg BW) induced increasing the JNK and ERK expressions (p < 0.05) and four proteins such as Destrin, Anionic trypsin-1, Trypsinogen, and especially eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 in rat pancreas.
Conclusions: Taken together, exogenous ghrelin by i.p. infusion plays a role in the pancreatic exocrine secretion via mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.
Keywords: Cholecystokinin; Ghrelin; Pancreatic exocrine; Sprague-Dawley rats; α-Amylase activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of proteins involved in the pancreatic exocrine by exogenous ghrelin administration in Sprague-Dawley rats.J Anim Sci Technol. 2014 Jun 5;56:6. doi: 10.1186/2055-0391-56-6. eCollection 2014. J Anim Sci Technol. 2014. PMID: 26290695 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of pancreatic protein secretion by ghrelin in the rat.J Physiol. 2001 Nov 15;537(Pt 1):231-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0231k.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11711576 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of luminal ghrelin on pancreatic enzyme secretion in the rat.Regul Pept. 2007 Oct 4;143(1-3):56-63. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2007.03.001. Epub 2007 Mar 14. Regul Pept. 2007. PMID: 17462749
-
Role of feed-regulating peptides on pancreatic exocrine secretion.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008 Aug;59 Suppl 2:145-59. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18812635 Review.
-
Ghrelin and melatonin in the regulation of pancreatic exocrine secretion and maintaining of integrity.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;57 Suppl 5:83-96. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17218761 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effects of ghrelin on pancreas in fructose diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.J Mol Histol. 2024 Dec 14;56(1):43. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10329-8. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 39673670
-
Impacts of whey protein on starch digestion in rumen and small intestine of steers.J Anim Sci Technol. 2019 Mar;61(2):98-108. doi: 10.5187/jast.2019.61.2.98. Epub 2019 Mar 31. J Anim Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 31333867 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

