Autophagy and inflammation
- PMID: 28748360
- PMCID: PMC5529308
- DOI: 10.1186/s40169-017-0154-5
Autophagy and inflammation
Abstract
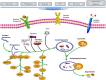
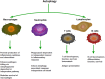
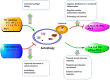
Autophagy is a homeostatic mechanism involved in the disposal of damaged organelles, denatured proteins as well as invaded pathogens through a lysosomal degradation pathway. Recently, increasing evidences have demonstrated its role in both innate and adaptive immunity, and thereby influence the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. The detection of autophagy machinery facilitated the measurement of autophagy during physiological and pathophysiological processes. Autophagy plays critical roles in inflammation through influencing the development, homeostasis and survival of inflammatory cells, including macrophages, neutrophils and lymphocytes; effecting the transcription, processing and secretion of a number of cytokines, as well as being regulated by cytokines. Recently, autophagy-dependent mechanisms have been studied in the pathogenesis of several inflammatory diseases, including infectious diseases, Crohn's disease, cystic fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases and so on. These studies suggested that modulation of autophagy might lead to therapeutic interventions for diseases associated with inflammation. Here we highlight recent advances in investigating the roles of autophagy in inflammation as well as inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Autophagy; Inflammation; Inflammatory diseases.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
