Anti-Oxidative Stress Activity Is Essential for Amanita caesarea Mediated Neuroprotection on Glutamate-Induced Apoptotic HT22 Cells and an Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Model
- PMID: 28749416
- PMCID: PMC5578015
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18081623
Anti-Oxidative Stress Activity Is Essential for Amanita caesarea Mediated Neuroprotection on Glutamate-Induced Apoptotic HT22 Cells and an Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Model
Abstract
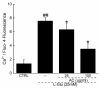
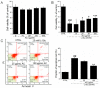
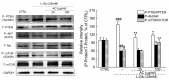
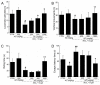
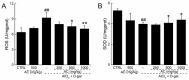
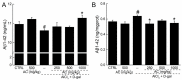
Amanita caesarea, an edible mushroom found mainly in Asia and southern Europe, has been reported to show good antioxidative activities. In the present study, the neuroprotective effects of A. caesarea aqueous extract (AC) were determined in an l-glutamic acid (l-Glu) induced HT22 cell apoptosis model, and in a d-galactose (d-gal) and AlCl₃-developed experimental Alzheimer's disease (AD) mouse model. In 25 mM of l-Glu-damaged HT22 cells, a 3-h pretreatment with AC strongly improved cell viability, reduced the proportion of apoptotic cells, restored mitochondrial function, inhibited the over-production of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and Ca2+, and suppressed the high expression levels of cleaved-caspase-3, calpain 1, apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) and Bax. Compared with HT22 exposed only to l-Glu cells, AC enhanced the phosphorylation activities of protein kinase B (Akt) and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and suppressed the phosphorylation activities of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten (PTEN). In the experimental AD mouse, 28-day AC administration at doses of 250, 500, and 1000 mg/kg/day strongly enhanced vertical movements and locomotor activities, increased the endurance time in the rotarod test, and decreased the escape latency time in the Morris water maze test. AC also alleviated the deposition of amyloid beta (Aβ) in the brain and improved the central cholinergic system function, as indicated by an increase acetylcholine (Ach) and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) concentrations and a reduction in acetylcholine esterase (AchE) levels. Moreover, AC reduced ROS levels and enhanced superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels in the brain of experimental AD mice. Taken together, our data provide experimental evidence that A. caesarea may serve as potential food for treating or preventing neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amanita caesarea; apoptosis; cholinergic transmitters; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacological Basis for the Use of Evodiamine in Alzheimer's Disease: Antioxidation and Antiapoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 21;19(5):1527. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051527. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29883380 Free PMC article.
-
The Neuroprotective Properties of Hericium erinaceus in Glutamate-Damaged Differentiated PC12 Cells and an Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Nov 1;17(11):1810. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111810. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27809277 Free PMC article.
-
Protective roles of Amanita caesarea polysaccharides against Alzheimer's disease via Nrf2 pathway.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Jan;121:29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.216. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30290256
-
Delineation of Neuroprotective Effects and Possible Benefits of AntioxidantsTherapy for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Diseases by Targeting Mitochondrial-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species: Bench to Bedside.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Jan;59(1):657-680. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02617-1. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 34751889 Review.
-
A review on ferulic acid and analogs based scaffolds for the management of Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Apr 5;215:113278. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113278. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33662757 Review.
Cited by
-
High-Dose Tanshinone IIA Suppresses Migration and Proliferation While Promoting Apoptosis of Astrocytoma Cells Via Notch-1 Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2018 Sep;43(9):1855-1861. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2601-0. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 30066161
-
Neuroprotective Effects against Glutamate-Induced HT-22 Hippocampal Cell Damage and Caenorhabditis elegans Lifespan/Healthspan Enhancing Activity of Auricularia polytricha Mushroom Extracts.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Sep 29;14(10):1001. doi: 10.3390/ph14101001. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681226 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy and apoptosis cascade: which is more prominent in neuronal death?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(24):8001-8047. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04004-4. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34741624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological Basis for the Use of Evodiamine in Alzheimer's Disease: Antioxidation and Antiapoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 21;19(5):1527. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051527. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29883380 Free PMC article.
-
Protective roles of isoastilbin against Alzheimer's disease via Nrf2‑mediated antioxidation and anti‑apoptosis.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Mar;43(3):1406-1416. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4058. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30664148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosello A., Warnes G., Meier U.C. Cell death pathways and autophagy in the central nervous system and its involvement in neurodegeneration, immunity and central nervous system infection: To die or not to die--that is the question. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012;168:52–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04544.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

