Comparison of hemolytic activity of the intermediate subunit of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar lectins
- PMID: 28750000
- PMCID: PMC5531476
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181864
Comparison of hemolytic activity of the intermediate subunit of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar lectins
Abstract
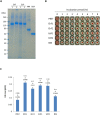
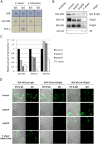
Galactose and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable lectin of Entamoeba histolytica has roles in pathogenicity and induction of protective immunity in rodent models of amoebiasis. Recently, the intermediate subunit of the lectin, Igl1, of E. histolytica has been shown to have hemolytic activity. However, the corresponding lectin is also expressed in a non-virulent species, Entamoeba dispar, and another subunit, Igl2, is expressed in the protozoa. Therefore, in this study, we compared the activities of Igl1 and Igl2 subunits from E. histolytica and E. dispar using various regions of recombinant Igl proteins expressed in Escherichia coli. The recombinant E. dispar Igl proteins had comparable hemolytic activities with those of E. histolytica Igl proteins. Furthermore, Igl1 gene-silenced E. histolytica trophozoites showed less hemolytic activity compared with vector-transfected trophozoites, indicating that the expression level of Igl1 protein influences the activity. These results suggest that the lower hemolytic activity in E. dispar compared with E. histolytica reflects the lower expression level of Igl1 in the E. dispar parasite.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Identification of Multiple Domains of Entamoeba histolytica Intermediate Subunit Lectin-1 with Hemolytic and Cytotoxic Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 12;23(14):7700. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147700. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887043 Free PMC article.
-
Novel hemagglutinating, hemolytic and cytotoxic activities of the intermediate subunit of Entamoeba histolytica lectin.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 10;5:13901. doi: 10.1038/srep13901. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26354528 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a carbohydrate recognition domain-like region in Entamoeba histolytica Gal/GalNAc lectin intermediate subunit.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Nov 5;12(11):e0053824. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00538-24. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39365081 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments in amoebiasis:the Gal/GalNAc lectins of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar.Microbes Infect. 2000 Nov;2(14):1775-83. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(00)01330-7. Microbes Infect. 2000. PMID: 11137050 Review.
-
The pathogenicity of Entamoeba histolytica is related to the capacity of evading innate immunity.Parasite Immunol. 2005 Jan-Feb;27(1-2):1-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2005.00743.x. Parasite Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15813717 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Multiple Domains of Entamoeba histolytica Intermediate Subunit Lectin-1 with Hemolytic and Cytotoxic Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 12;23(14):7700. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147700. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887043 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble expression of an amebic cysteine protease in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli SHuffle Express cells and purification of active enzyme.BMC Biotechnol. 2018 Apr 3;18(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12896-018-0429-y. BMC Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29615011 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Phosphatase PP2C Identification in Entamoeba spp.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Oct 16;2021:5746629. doi: 10.1155/2021/5746629. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34697588 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between human mucins and parasite glycoproteins: the role of lectins and glycosidases in colonization by intestinal protozoa.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2020 Sep 4;62:e64. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946202062064. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2020. PMID: 32901761 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome sequencing of Entamoeba nuttalli reveals mammalian host-related molecular signatures and a novel octapeptide-repeat surface protein.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Dec 5;13(12):e0007923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007923. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31805050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stanley SL Jr. Amoebiasis. Lancet. 2003; 361: 1025–1034. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12830-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Petri WA Jr, Haque R, Mann BJ. The bittersweet interface of parasite and host: lectin-carbohydrate interactions during human invasion by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2002; 56: 39–64. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160959 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Laughlin RC, McGugan GC, Powell RR, Welter BH, Temesvari LA. Involvement of Raft-Like Plasma Membrane Domains of Entamoeba histolytica in Pinocytosis and Adhesion. Infect Immun. 2004; 72: 5349–5357. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5349-5357.2004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Welter BH, Goldston AM, Temesvari LA. Localisation to lipid rafts correlates with increased function of the Gal/GalNAc lectin in the human protozoan parasite. Entamoeba histolytica, Int J Parasitol. 2011; 41: 1409–1419. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2011.10.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng XJ, Tsukamoto H, Kaneda Y, Tachibana H. Identification of the 150-kDa surface antigen of Entamoeba histolytica as a galactose- and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable lectin. Parasitol Res. 1998; 84: 632–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

