Target specificity, in vivo pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of the putative STAT3 inhibitor LY5 in osteosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, and rhabdomyosarcoma
- PMID: 28750090
- PMCID: PMC5531494
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181885
Target specificity, in vivo pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of the putative STAT3 inhibitor LY5 in osteosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, and rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
Background: STAT3 is a transcription factor involved in cytokine and receptor kinase signal transduction that is aberrantly activated in a variety of sarcomas, promoting metastasis and chemotherapy resistance. The purpose of this work was to develop and test a novel putative STAT3 inhibitor, LY5.
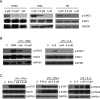
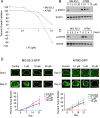
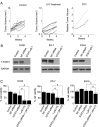
Methods and findings: An in silico fragment-based drug design strategy was used to create LY5, a small molecule inhibitor that blocks the STAT3 SH2 domain phosphotyrosine binding site, inhibiting homodimerization. LY5 was evaluated in vitro demonstrating good biologic activity against rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma cell lines at high nanomolar/low micromolar concentrations, as well as specific inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation without effects on other STAT3 family members. LY5 exhibited excellent oral bioavailability in both mice and healthy dogs, and drug absorption was enhanced in the fasted state with tolerable dosing in mice at 40 mg/kg BID. However, RNAi-mediated knockdown of STAT3 did not phenocopy the biologic effects of LY5 in sarcoma cell lines. Moreover, concentrations needed to inhibit ex vivo metastasis growth using the PuMA assay were significantly higher than those needed to inhibit STAT3 phosphorylation in vitro. Lastly, LY5 treatment did not inhibit the growth of sarcoma xenografts or prevent pulmonary metastasis in mice.
Conclusions: LY5 is a novel small molecule inhibitor that effectively inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation and cell proliferation at nanomolar concentrations. LY5 demonstrates good oral bioavailability in mice and dogs. However LY5 did not decrease tumor growth in xenograft mouse models and STAT3 knockdown did not induce concordant biologic effects. These data suggest that the anti-cancer effects of LY5 identified in vitro were not mediated through STAT3 inhibition.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
A novel small molecular STAT3 inhibitor, LY5, inhibits cell viability, cell migration, and angiogenesis in medulloblastoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 6;290(6):3418-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.616748. Epub 2014 Oct 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25313399 Free PMC article.
-
A novel small molecule STAT3 inhibitor, LY5, inhibits cell viability, colony formation, and migration of colon and liver cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 15;7(11):12917-26. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7338. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26883202 Free PMC article.
-
Dasatinib inhibits migration and invasion in diverse human sarcoma cell lines and induces apoptosis in bone sarcoma cells dependent on SRC kinase for survival.Cancer Res. 2007 Mar 15;67(6):2800-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3469. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17363602
-
Chemotherapy in the management of osteosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma.J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2007 Apr;5(4):449-55. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2007.0039. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2007. PMID: 17442235 Review.
-
The value of adjuvant chemotherapy in the management of sarcomas in children.Cancer. 1985 May 1;55(9 Suppl):2184-97. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850501)55:9+<2184::aid-cncr2820551422>3.0.co;2-n. Cancer. 1985. PMID: 3884137 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of TORC1 by MAPK Signaling Determines Sensitivity and Acquired Resistance to Trametinib in Pediatric BRAFV600E Brain Tumor Models.Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Sep 1;28(17):3836-3849. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-1052. Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35797217 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the metabolic role of STAT3 in canine osteosarcoma.Vet Comp Oncol. 2022 Dec;20(4):817-824. doi: 10.1111/vco.12841. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Vet Comp Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35608271 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium cantharidate targets STAT3 and abrogates EGFR inhibitor resistance in osteosarcoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Aug 15;11(15):5848-5863. doi: 10.18632/aging.102193. Epub 2019 Aug 15. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31422383 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6 and CXCL8 mediate osteosarcoma-lung interactions critical to metastasis.JCI Insight. 2018 Aug 23;3(16):e99791. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.99791. eCollection 2018 Aug 23. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 30135299 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 and its targeting inhibitors in osteosarcoma.Cell Prolif. 2021 Feb;54(2):e12974. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12974. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Cell Prolif. 2021. PMID: 33382511 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arndt CA, Rose PS, Folpe AL, Laack NN. Common musculoskeletal tumors of childhood and adolescence. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87(5):475–87. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.01.015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hosoi H. Current status of treatment for pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma in the USA and Japan. Pediatrics international: official journal of the Japan Pediatric Society. 2016;58(2):81–7. - PubMed
-
- Yu H, Ge Y, Guo L, Huang L. Potential approaches to the treatment of Ewing's sarcoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(3):5523–39. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12566 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen CL, Loy A, Cen L, Chan C, Hsieh FC, Cheng G, et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is involved in cell growth and survival of human rhabdomyosarcoma and osteosarcoma cells. BMC cancer. 2007;7:111 doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-111 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fossey SL, Liao AT, McCleese JK, Bear MD, Lin J, Li PK, et al. Characterization of STAT3 activation and expression in canine and human osteosarcoma. BMC cancer. 2009;9:81 doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-81 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

