Vision-Related Functional Burden of Diabetic Retinopathy Across Severity Levels in the United States
- PMID: 28750122
- PMCID: PMC5710538
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.2553
Vision-Related Functional Burden of Diabetic Retinopathy Across Severity Levels in the United States
Abstract
Importance: Among adults with diabetes in the United States, severe forms of diabetic retinopathy (DR) are significantly associated with a greater vision-related functional burden.
Objective: To assess the functional burden of DR across severity levels in the United States.
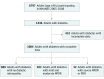
Design, setting, and participants: This cross-sectional study was based on 1004 participants 40 years or older with diabetes and valid ocular and sociodemographic outcomes in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) (2005-2006 and 2007-2008). Diabetic retinopathy was based on fundus photograph grading, using the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study severity scale. The analysis was performed from October 15, 2016, to June 15, 2017.
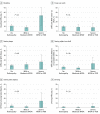
Main outcomes and measures: Functional difficulties secondary to vision were assessed during a household questionnaire in which participants self-reported difficulty with reading, visuospatial tasks (ie, close-up work or finding things on a crowded shelf), mobility (ie, walking down steps, stairs, or curbs), and driving. The main outcome measure was vision-related functional burden, which was defined as present for individuals reporting moderate or greater difficulty in any of the aforementioned tasks.
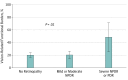
Results: Of the 1004 persons with diabetes analyzed for this study (mean age, 65.7 years [95% CI, 64.0-67.3 years]; 51.1% male [95% CI, 47.1-55.2] and 48.9% female [95% CI, 44.8-52.9]), the prevalence was 72.3% for no retinopathy, 25.4% for mild and moderate nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR), and 2.3% for severe NPDR or proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). The prevalence of vision-related functional burden was 20.2% (95% CI, 16.3%-24.1%) for those with no retinopathy, 20.4% (95% CI, 15.3%-27.8%) for those with mild and moderate NPDR, and 48.5% (95% CI, 25.6%-71.5%) for those with severe NPDR or PDR (P = .02). In multivariable analysis, the odds of vision-related functional burden were significantly greater among those with severe NPDR or PDR relative to those with no retinopathy (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 3.59; 95% CI, 1.29-10.05; P = .02). Those with severe NPDR or PDR did not have a statistically significant greater odds of vision-related functional burden than did those with mild or moderate NPDR (aOR, 2.70; 95% CI, 0.93-7.78; P = .07).
Conclusions and relevance: Among US adults with diabetes, approximately half of those with severe NPDR or PDR had difficulty with at least one visual function task. Moreover, vision-related functional burden was significantly greater among those with severe NPDR or PDR than among those with no retinopathy. These data suggest the importance of preventing severe forms of DR to mitigate the vision-related functional burden among US adults with diabetes. Future studies should complement our study by assessing the association of worsening retinopathy with objectively measured functional outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Potential Confounders in an Investigation of the Vision-Related Functional Burden of Diabetic Retinopathy.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018 Apr 1;136(4):450. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.6703. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29450482 No abstract available.
-
Potential Confounders in an Investigation of the Vision-Related Functional Burden of Diabetic Retinopathy-Reply.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018 Apr 1;136(4):450-451. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.6573. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29450491 No abstract available.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Vision Health Initiative (VHI) Report: Projection of Diabetic Retinopathy and Other Major Eye Diseases among People with Diabetes Mellitus United States, 2005-2050. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2015.
-
- Coyne KS, Margolis MK, Kennedy-Martin T, et al. The impact of diabetic retinopathy: perspectives from patient focus groups. Fam Pract. 2004;21(4):447-453. - PubMed
-
- Sharma S, Oliver-Fernandez A, Liu W, Buchholz P, Walt J. The impact of diabetic retinopathy on health-related quality of life. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2005;16(3):155-159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

