Characterization of Small-Molecule Scaffolds That Bind to the Shigella Type III Secretion System Protein IpaD
- PMID: 28750143
- PMCID: PMC5741093
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201700348
Characterization of Small-Molecule Scaffolds That Bind to the Shigella Type III Secretion System Protein IpaD
Abstract
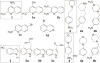
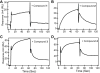
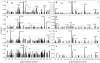
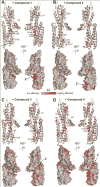
Many pathogens such as Shigella and other bacteria assemble the type III secretion system (T3SS) nanoinjector to inject virulence proteins into their target cells to cause infectious diseases in humans. The rise of drug resistance among pathogens that rely on the T3SS for infectivity, plus the dearth of new antibiotics require alternative strategies in developing new antibiotics. The Shigella T3SS tip protein IpaD is an attractive target for developing anti-infectives because of its essential role in virulence and its exposure on the bacterial surface. Currently, the only known small molecules that bind to IpaD are bile salt sterols. In this study we identified four new small-molecule scaffolds that bind to IpaD, based on the methylquinoline, pyrrolidine-aniline, hydroxyindole, and morpholinoaniline scaffolds. NMR mapping revealed potential hotspots in IpaD for binding small molecules. These scaffolds can be used as building blocks in developing small-molecule inhibitors of IpaD that could lead to new anti-infectives.
Keywords: IpaD; NMR spectroscopy; small molecules; surface plasmon resonance; type III secretion system.
© 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of the Binding of Hydroxyindole, Indoleacetic acid, and Morpholinoaniline to the Salmonella Type III Secretion System Proteins SipD and SipB.ChemMedChem. 2016 May 6;11(9):963-71. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201600065. Epub 2016 Mar 18. ChemMedChem. 2016. PMID: 26990667 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterization of the IpaD π-helix reveals critical roles in DOC interaction, T3SS apparatus maturation, and Shigella virulence.J Biol Chem. 2024 Sep;300(9):107613. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107613. Epub 2024 Jul 28. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39079629 Free PMC article.
-
NMR identification of the binding surfaces involved in the Salmonella and Shigella Type III secretion tip-translocon protein-protein interactions.Proteins. 2016 Aug;84(8):1097-107. doi: 10.1002/prot.25055. Epub 2016 May 5. Proteins. 2016. PMID: 27093649 Free PMC article.
-
The Many Faces of IpaB.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Feb 9;6:12. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00012. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26904511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the Type III Secretion System.Molecules. 2015 Sep 23;20(9):17659-74. doi: 10.3390/molecules200917659. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26404233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Possible drugs for the treatment of bacterial infections in the future: anti-virulence drugs.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2021 Jan;74(1):24-41. doi: 10.1038/s41429-020-0344-z. Epub 2020 Jul 9. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2021. PMID: 32647212 Review.
-
Promises and Challenges of the Type Three Secretion System Injectisome as an Antivirulence Target.EcoSal Plus. 2019 Feb;8(2):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0032-2018. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0032-2018. EcoSal Plus. 2019. PMID: 30706846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secretory System Components as Potential Prophylactic Targets for Bacterial Pathogens.Biomolecules. 2021 Jun 15;11(6):892. doi: 10.3390/biom11060892. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34203937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting bacterial pathogenesis by inhibiting virulence-associated Type III and Type IV secretion systems.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jan 10;12:1065561. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1065561. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36704108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Targets and Strategies for Inhibition of the Bacterial Type III Secretion System (T3SS); Inhibitors Directly Binding to T3SS Components.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 19;11(2):316. doi: 10.3390/biom11020316. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33669653 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kotloff KL, Nataro JP, Blackwelder WC, Nasrin D, Farag TH, Panchalingam S, Wu Y, Sow SO, Sur D, Breiman RF, Faruque AS, Zaidi AK, Saha D, Alonso PL, Tamboura B, Sanogo D, Onwuchekwa U, Manna B, Ramamurthy T, Kanungo S, Ochieng JB, Omore R, Oundo JO, Hossain A, Das SK, Ahmed S, Qureshi S, Quadri F, Adegbola RA, Antonio M, Hossain MJ, Akinsola A, Mandomando I, Nhampossa T, Acacio S, Biswas K, O’Reilly CE, Mintz ED, Berkeley LY, Muhsen K, Sommerfelt H, Robins-Browne RM, Levine MM. Lancet. 2013;382:209–222. - PubMed
-
- Galan JE, Wolf-Watz H. Nature. 2006;444:567–573. - PubMed
-
- Epler CR, Dickenson NE, Bullitt E, Picking WL. J Mol Biol. 2012;420:29–39. - PMC - PubMed
- Espina M, Olive AJ, Kenjale R, Moore DS, Ausar SF, Kaminski RW, Oaks EV, Middaugh CR, Picking WD, Picking WL. Infect Immun. 2006;74:4391–4400. - PMC - PubMed
- Roehrich AD, Guillossou E, Blocker AJ, Martinez-Argudo I. Mol Microbiol. 2013;87:690–706. - PMC - PubMed
- Meghraoui A, Schiavolin L, Allaoui A. Microbes Infect. 2014;16:532–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

