Single-Center Evaluation of the Pharmacokinetics and Safety of the Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist Azilsartan Medoxomil in Mild to Moderate Hepatic Impairment
- PMID: 28750149
- PMCID: PMC5763333
- DOI: 10.1002/jcph.970
Single-Center Evaluation of the Pharmacokinetics and Safety of the Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist Azilsartan Medoxomil in Mild to Moderate Hepatic Impairment
Abstract
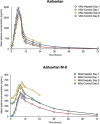
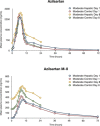
Azilsartan medoxomil (AZL-M) is a potent angiotensin II receptor blocker that decreases blood pressure in a dose-dependent manner. It is a prodrug that is not detected in blood after its oral administration because of its rapid hydrolysis to the active moiety, azilsartan (AZL). AZL undergoes further metabolism to the major metabolite, M-II, and minor metabolites. The objective of this study was to determine the effect of mild to moderate hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of AZL and its major metabolite. This was a single-center, open-label, phase 1 parallel-group study that examined the single-dose (day 1) and multiple-dose (days 4-8) - 40 mg - pharmacokinetics of AZL and M-II in 16 subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment by Child-Pugh classification (n = 8 per group) and subjects (n = 16) matched based on age, sex, race, weight, and smoking status. Mild or moderate hepatic impairment did not cause clinically meaningful increases in exposure to AZL and M-II. Mild or moderate hepatic impairment had no clinically meaningful effect on the plasma protein binding of AZL and M-II. Single and multiple doses of AZL-M 40 mg were well tolerated in all subject groups. Based on the pharmacokinetic and tolerability findings, no dose adjustment of AZL-M is required for subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment.
Keywords: angiotensin II receptor blocker; azilsartan medoxomil; drug metabolism; hepatic impairment; hypertension; pharmacokinetics.
© 2017, The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

