The Effect of Intragastric Administration of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Reducing Adiposity in a Rat Model of Obesity Using Micro-CT and Histological Examinations
- PMID: 28750487
- PMCID: PMC5669595
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl16557
The Effect of Intragastric Administration of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Reducing Adiposity in a Rat Model of Obesity Using Micro-CT and Histological Examinations
Abstract
Background/aims: Botulinum toxin type A (BTX), a long-acting inhibitor of muscular contraction in both striated and smooth muscles, is responsible for gastric motility. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of an endoscopic intragastric BTX injection on weight loss, body fat accumulation, and gastric emptying time.
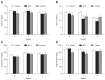
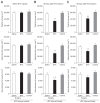
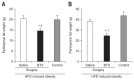
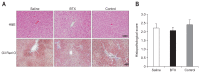
Methods: The BTX group consisted of 15 obese rats in which 20 U of BTX were injected into the gastric antrum. The saline group consisted of 15 obese rats injected with 20 U of saline, and the control group included 10 obese rats that did not receive a surgical intervention. The gastric emptying time, biochemical parameters, and body fat volume were evaluated using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) and histologic evaluations.
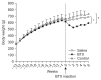
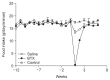
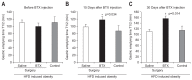
Results: The postoperative body weight of the BTX group was significantly lower than those of the other groups (p<0.001) at 6 weeks after the operation. The gastric emptying time (156±54 minutes) was significantly delayed in the BTX group. The BTX group showed significantly lower lipid levels than the other groups. A reduction in body fat volume was observed in the BTX group using micro-CT and histological evaluations.
Conclusions: BTX application to the gastric antrum represents a potentially effective treatment for obesity and may help improve the lipid profile by increasing the gastric emptying time.
Keywords: Botulinum toxins; Endoscopes; Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intragastric injection of botulinum toxin A for the treatment of obesity.Obes Surg. 2007 Jun;17(6):732-6. doi: 10.1007/s11695-007-9135-x. Obes Surg. 2007. PMID: 17879570 Clinical Trial.
-
EUS-Guided Intragastric Injection of Botulinum Toxin A in the Preoperative Treatment of Super-Obese Patients: a Randomized Clinical Trial.Obes Surg. 2019 Jan;29(1):32-39. doi: 10.1007/s11695-018-3470-y. Obes Surg. 2019. PMID: 30120640 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of botulinum toxin antral injection on gastric emptying and weight reduction in obese patients: a pilot study.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Mar 1;23(5):675-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.02773.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16480407 Clinical Trial.
-
The Role of Endoscopic Intra-Gastric Botulinum Toxin-A for Obesity Treatment.Obes Surg. 2017 Sep;27(9):2471-2478. doi: 10.1007/s11695-017-2806-3. Obes Surg. 2017. PMID: 28685363 Review.
-
Intragastric injection of botulinum toxin A for weight loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;37(6):983-992. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15847. Epub 2022 Apr 22. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35383416
Cited by
-
How Taking into Account the Pyloric Tonus Contributes to Treatment Success While Administering Gastric "Botulinum Toxin A" for Weight Loss.Obes Surg. 2020 Sep;30(9):3365-3369. doi: 10.1007/s11695-020-04556-7. Obes Surg. 2020. PMID: 32405906
-
Effect of Intragastric Botulinum Type A Injection Combined with a Low-Calorie High-Protein Diet in Adults with Overweight or Obesity.J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 10;11(12):3325. doi: 10.3390/jcm11123325. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35743396 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs in focus: Botulinum toxin in the therapy of gastrointestinal disorders in children.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2024 Dec;79(6):1096-1105. doi: 10.1002/jpn3.12376. Epub 2024 Sep 24. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39315663 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Botulinum Toxin in Experimental Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2021 Dec;31(12):1460-1465. doi: 10.1089/lap.2021.0308. Epub 2021 Nov 16. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2021. PMID: 34788135 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic Botulinum Therapy for Obesity: Focus on the Antrum and Fundus.Cureus. 2025 Jul 5;17(7):e87319. doi: 10.7759/cureus.87319. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40761969 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

