Non-genomic transmission of longevity between generations: potential mechanisms and evidence across species
- PMID: 28750655
- PMCID: PMC5531095
- DOI: 10.1186/s13072-017-0145-1
Non-genomic transmission of longevity between generations: potential mechanisms and evidence across species
Abstract
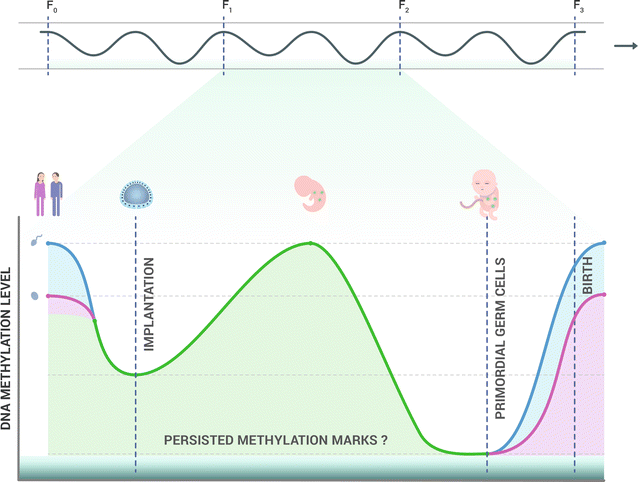
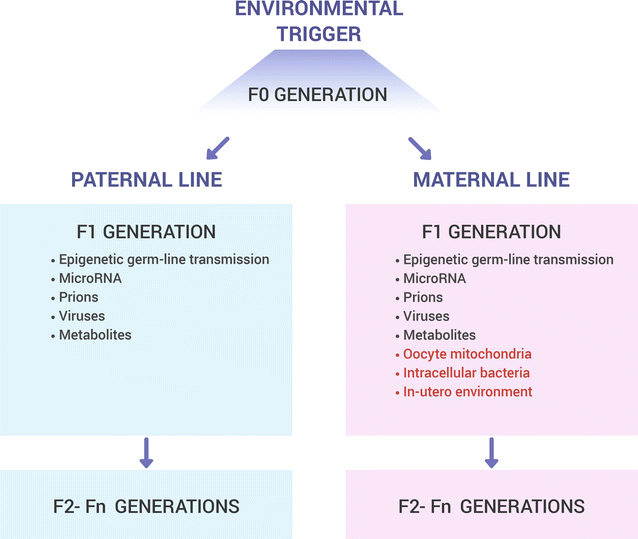
Accumulating animal and human data indicate that environmental exposures experienced during sensitive developmental periods may strongly influence risk of adult disease. Moreover, the effects triggered by developmental environmental cues can be transgenerationally transmitted, potentially affecting offspring health outcomes. Increasing evidence suggests a central role of epigenetic mechanisms (heritable alterations in gene expression occurring without changes in underlying DNA sequence) in mediating these effects. This review summarizes the findings from animal models, including worms, insects, and rodents, and also from human studies, indicating that lifespan and longevity-associated characteristics can be transmitted across generations via non-genetic factors.
Keywords: Age-associated disease; Aging; DNA methylation; Epigenetics; Longevity; Transgenerational inheritance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insects as models to study the epigenetic basis of disease.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;118(1-2):69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2015.02.009. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25778758 Review.
-
Progress on the role of DNA methylation in aging and longevity.Brief Funct Genomics. 2016 Nov;15(6):454-459. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elw009. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Brief Funct Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27032421 Review.
-
Lamarck rises from his grave: parental environment-induced epigenetic inheritance in model organisms and humans.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2017 Nov;92(4):2084-2111. doi: 10.1111/brv.12322. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2017. PMID: 28220606 Review.
-
An evolutionary perspective of lifespan and epigenetic inheritance.Exp Gerontol. 2023 Aug;179:112256. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2023.112256. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Exp Gerontol. 2023. PMID: 37460026 Review.
-
Developmental programming and transgenerational transmission of obesity.Ann Nutr Metab. 2014;64 Suppl 1:26-34. doi: 10.1159/000360506. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Ann Nutr Metab. 2014. PMID: 25059803
Cited by
-
Developmental alterations in DNA methylation during gametogenesis from primordial germ cells to sperm.iScience. 2022 Jan 19;25(2):103786. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103786. eCollection 2022 Feb 18. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35146397 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation changes induced by prenatal toxic metal exposure: An overview of epidemiological evidence.Environ Epigenet. 2021 Oct 6;7(1):dvab007. doi: 10.1093/eep/dvab007. eCollection 2021. Environ Epigenet. 2021. PMID: 34631153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific Differentially Methylated and Expressed Genes in People with Longevity Family History.Iran J Public Health. 2021 Jan;50(1):152-160. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v50i1.5082. Iran J Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34178774 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Virus Infection on Microglia and Accelerated Brain Aging.Cells. 2021 Jul 20;10(7):1836. doi: 10.3390/cells10071836. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34360004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early-life adversity and long-term neurobehavioral outcomes: epigenome as a bridge?Hum Genomics. 2017 Dec 16;11(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40246-017-0129-z. Hum Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29246185 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weismann A. The germ-plasm: a theory of heredity. Translated by W. Newton Parker and Harriet Rönnfeldt. New York: Scribner; 1893.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

