The Impact of Cryoballoon Versus Radiofrequency Ablation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation on Healthcare Utilization and Costs: An Economic Analysis From the FIRE AND ICE Trial
- PMID: 28751544
- PMCID: PMC5586445
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006043
The Impact of Cryoballoon Versus Radiofrequency Ablation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation on Healthcare Utilization and Costs: An Economic Analysis From the FIRE AND ICE Trial
Erratum in
-
The Impact of Cryoballoon Versus Radiofrequency Ablation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation on Healthcare Utilization and Costs: An Economic Analysis From the FIRE AND ICE Trial.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Sep 15;6(9):e002230. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.002230. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28916528 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: This study sought to assess payer costs following cryoballoon or radiofrequency current (RFC) catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in the randomized FIRE AND ICE trial.
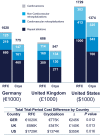
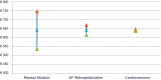
Methods and results: A trial period analysis of healthcare costs evaluated the impact of ablation modality (cryoballoon versus RFC) on differences in resource use and associated payer costs. Analyses were based on repeat interventions, rehospitalizations, and cardioversions during the trial, with unit costs based on 3 national healthcare systems (Germany [€], the United Kingdom [£], and the United States [$]). Total payer costs were calculated by applying standard unit costs to hospital stays, using International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision diagnoses and procedure codes that were mapped to country-specific diagnosis-related groups. Patients (N=750) randomized 1:1 to cryoballoon (n=374) or RFC (n=376) ablation were followed for a mean of 1.5 years. Resource use was lower in the cryoballoon than the RFC group (205 hospitalizations and/or interventions in 122 patients versus 268 events in 154 patients). The cost differences per patient in mean total payer costs during follow-up were €640, £364, and $925 in favor of cryoballoon ablation (P=0.012, 0.013, and 0.016, respectively). This resulted in trial period total cost savings of €245 000, £140 000, and $355 000.
Conclusions: When compared with RFC ablation, cryoballoon ablation was associated with a reduction in resource use and payer costs. In all 3 national healthcare systems analyzed, this reduction resulted in substantial trial period cost savings, primarily attributable to fewer repeat ablations and a reduction in cardiovascular rehospitalizations with cryoballoon ablation.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Identifier: NCT01490814.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; catheter ablation; cryoballoon; health economics; pulmonary vein isolation.
© 2017 The Authors and Medtronic. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures

References
-
- McBride D, Mattenklotz A, Willich S, Brüggenjürgen B. The costs of care in atrial fibrillation and the effect of treatment modalities in Germany. Value Health. 2009;12:293–301. - PubMed
-
- Kim MH, Johnston SS, Chu BC, Dalal MR, Schulman KL. Estimation of total incremental health care costs in patients with atrial fibrillation in the United States. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2011;4:313–320. - PubMed
-
- Calkins H, Kuck KH, Cappato R, Brugada J, Camm AJ, Chen SA, Crijns HJ, Damiano RJ Jr, Davies DW, DiMarco J, Edgerton J, Ellenbogen K, Ezekowitz MD, Haines DE, Haissaguerre M, Hindricks G, Iesaka Y, Jackman W, Jalife J, Jais P, Kalman J, Keane D, Kim YH, Kirchhof P, Klein G, Kottkamp H, Kumagai K, Lindsay BD, Mansour M, Marchlinski FE, McCarthy PM, Mont JL, Morady F, Nademanee K, Nakagawa H, Natale A, Nattel S, Packer DL, Pappone C, Prystowsky E, Raviele A, Reddy V, Ruskin JN, Shemin RJ, Tsao HM, Wilber D. 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow‐up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2012;33:171–257. - PubMed
-
- Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B, Castella M, Diener HC, Heidbuchel H, Hendriks J, Hindricks G, Manolis AS, Oldgren J, Popescu BA, Schotten U, Van Putte B, Vardas P, Agewall S, Camm J, Baron Esquivias G, Budts W, Carerj S, Casselman F, Coca A, De Caterina R, Deftereos S, Dobrev D, Ferro JM, Filippatos G, Fitzsimons D, Gorenek B, Guenoun M, Hohnloser SH, Kolh P, Lip GY, Manolis A, McMurray J, Ponikowski P, Rosenhek R, Ruschitzka F, Savelieva I, Sharma S, Suwalski P, Tamargo JL, Taylor CJ, Van Gelder IC, Voors AA, Windecker S, Zamorano JL, Zeppenfeld K. 2016 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2893–2962. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

