A deletion affecting an LRR-RLK gene co-segregates with the fruit flat shape trait in peach
- PMID: 28751691
- PMCID: PMC5532255
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-07022-0
A deletion affecting an LRR-RLK gene co-segregates with the fruit flat shape trait in peach
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: A deletion affecting an LRR-RLK gene co-segregates with the fruit flat shape trait in peach.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 30;12(1):5409. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09334-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35354892 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
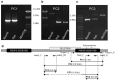
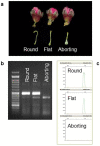
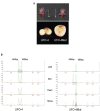
In peach, the flat phenotype is caused by a partially dominant allele in heterozygosis (Ss), fruits from homozygous trees (SS) abort a few weeks after fruit setting. Previous research has identified a SSR marker (UDP98-412) highly associated with the trait, found suitable for marker assisted selection (MAS). Here we report a ∼10 Kb deletion affecting the gene PRUPE.6G281100, 400 Kb upstream of UDP98-412, co-segregating with the trait. This gene is a leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase (LRR-RLK) orthologous to the Brassinosteroid insensitive 1-associated receptor kinase 1 (BAK1) group. PCR markers suitable for MAS confirmed its strong association with the trait in a collection of 246 cultivars. They were used to evaluate the DNA from a round fruit derived from a somatic mutation of the flat variety 'UFO-4', revealing that the mutation affected the flat associated allele (S). Protein BLAST alignment identified significant hits with genes involved in different biological processes. Best protein hit occurred with AtRLP12, which may functionally complement CLAVATA2, a key regulator that controls the stem cell population size. RT-PCR analysis revealed the absence of transcription of the partially deleted allele. The data support PRUPE.6G281100 as a candidate gene for flat shape in peach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Iglesias I. El melocotón plano en España: 15 años de innovación tecnológica y comercial. Revista de Fruticultura. 2014;35:6–31.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

