Astaxanthin ameliorates ferric nitrilotriacetate-induced renal oxidative injury in rats
- PMID: 28751805
- PMCID: PMC5525010
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.16-114
Astaxanthin ameliorates ferric nitrilotriacetate-induced renal oxidative injury in rats
Abstract
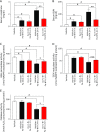
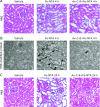
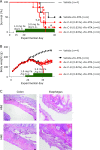
Daily intake of vegetables can reduce the risk of cancer and lifestyle-related diseases. However, supplementary intake of β-carotene alone has been reported to increase the risk of lung cancer in male cigarette smokers and people who were exposed to asbestos. The mechanism of the antioxidative properties of carotenoids in vivo, especially under oxidative stress conditions, still remains unclear. To investigate the antioxidant properties of dietary compounds, we examined the effects of chemically modified astaxanthin (Ax-C-8) using a rat model of ferric nitrilotriacetate (Fe-NTA)-induced renal oxidative injury. Ax-C-8 demonstrated lethally toxic effects on the rats in a dose-dependent manner. Following supplementation with Ax-C-8 (0.02%, w/w) for 30 days, the rats were euthanized 1, 4 and 24 h after injection of Fe-NTA. After 4 h, Ax-C-8 pretreatment suppressed the elevation of creatinine and blood urea nitrogen and protected the rats from renal tubular necrosis and the formation of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-modified proteins. After 24 h, pretreatment with Ax-C-8 maintained the renal antioxidant enzyme levels and renal tubules. Here, we demonstrate the antioxidant effects of Ax-C-8 against Fe-NTA-induced oxidative injury in rats receiving a regular diet. These data suggest that dietary intake of astaxanthin may be useful for the prevention of renal tubular oxidative damage.
Keywords: astaxanthin; ferric nitrilotriacetate; oxidative stress; vitamin E.
Conflict of interest statement
Research grant was provided from the Institute for Health Care Science, Suntory (Osaka, Japan).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bovine lactoferrin ameliorates ferric nitrilotriacetate-induced renal oxidative damage in rats.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2012 Sep;51(2):84-90. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.11-100. Epub 2012 Aug 4. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22962523 Free PMC article.
-
alpha-Tocopherol (vitamin-E) ameliorates ferric nitrilotriacetate (Fe-NTA)-dependent renal proliferative response and toxicity: diminution of oxidative stress.Hum Exp Toxicol. 1998 Mar;17(3):163-71. doi: 10.1177/096032719801700307. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1998. PMID: 9587785
-
A beverage containing fermented black soybean ameliorates ferric nitrilotriacetate-induced renal oxidative damage in rats.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010 Nov;47(3):198-207. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.10-52. Epub 2010 Sep 16. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010. PMID: 21103028 Free PMC article.
-
Diet and obstructive lung diseases.Epidemiol Rev. 2001;23(2):268-87. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a000806. Epidemiol Rev. 2001. PMID: 12192737 Review.
-
Astaxanthin as a Potential Protector of Liver Function: A Review.J Clin Med Res. 2016 Oct;8(10):701-4. doi: 10.14740/jocmr2672w. Epub 2016 Aug 30. J Clin Med Res. 2016. PMID: 27635173 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of astaxanthin against contrast-induced acute kidney injury via SIRT1-p53 pathway in rats.Int Urol Nephrol. 2019 Feb;51(2):351-358. doi: 10.1007/s11255-018-2027-2. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30456546
-
The Protective Effects of Astaxanthin on the OVA-Induced Asthma Mice Model.Molecules. 2017 Nov 21;22(11):2019. doi: 10.3390/molecules22112019. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29160801 Free PMC article.
-
Astaxanthin, a xanthophyll carotenoid, prevents development of dextran sulphate sodium-induced murine colitis.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2019 Jan;64(1):66-72. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.18-47. Epub 2018 Aug 11. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30705514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diplock AT, Charleux JL, Crozier-Willi G, et al. Functional food science and defence against reactive oxidative species. Br J Nutr. 1998;80 Suppl 1:S77–S112. - PubMed
-
- Omenn GS, Goodman G, Thornquist M, et al. The beta-carotene and retinol efficacy trial (CARET) for chemoprevention of lung cancer in high risk populations: smokers and asbestos-exposed workers. Cancer Res. 1994;54 (7 Suppl):2038s–2043s. - PubMed
-
- Omenn GS, Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, et al. Effects of a combination of beta carotene and vitamin A on lung cancer and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:1150–1155. - PubMed
-
- Kavanaugh CJ, Trumbo PR, Ellwood KC. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s evidence-based review for qualified health claims: tomatoes, lycopene, and cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:1074–1085. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

