Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Qingre-Qushi Recipe (QRQS) against Atopic Dermatitis: Potential Mechanism of Inhibition of IL-33/ST2 Signal Transduction
- PMID: 28751921
- PMCID: PMC5511684
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/2489842
Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Qingre-Qushi Recipe (QRQS) against Atopic Dermatitis: Potential Mechanism of Inhibition of IL-33/ST2 Signal Transduction
Abstract
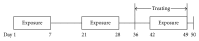
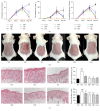
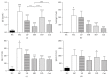
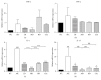
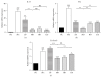
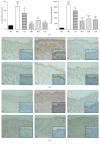
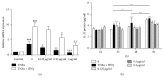
To evaluate the anti-inflammatory activities of QRQS against AD and the inhibitory molecular mechanisms of IL-33/ST2 signal transduction, BALB/c mice were divided into six groups (normal control, OVA control, low-dose of QRQS, middle-dose of QRQS, high-dose of QRQS, and cetirizine) and epicutaneously exposed to ovalbumin or PBS for 3 weeks and treated with QRQS for 2 weeks. Skin biopsies and blood samples were obtained for histological study, antibody analysis, and RNA isolation. HaCaT cells, stimulated by TNF-α and IFN-γ, were treated with QRQS to evaluate mRNA and protein expression by RT-PCR and ELISA. QRQS decreased both epidermal and dermal thickness, alleviated dermatitis, and reduced IL-33 and ST2 positive cell numbers. The concentration of specific IgE, IgG, IgG1, and IgG2a antibodies in serum and the expression of IL-33, ST2, IL-1RAcP, IL-4, and IL-13 mRNA in the skin were suppressed. No significant difference exists in TNF-α or IFN-γ. QRQS decreased IL-33 mRNA and protein secretion in HaCaT cells exposed to TNF-α and IFN-γ in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. QRQS regulates related molecule expression of ovalbumin-induced dermatitis involved in the IL-33/ST2 signaling axis in the treatment of acute AD.
Figures
References
-
- Du H.-Y., Fu H.-Y., Li D.-N., Qiao Y., Wang Q.-W., Liu W. The expression and regulation of interleukin-33 in human epidermal keratinocytes: a new mediator of atopic dermatitis and its possible signaling pathway. Journal of Interferon and Cytokine Research. 2016;36(9):552–562. doi: 10.1089/jir.2015.0159. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

