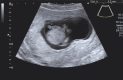
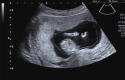
Is there any relationship between low PAPP-A levels and measures of umbilical vein and placental thickness during first trimester of pregnancy?
- PMID: 28752144
- PMCID: PMC5530159
- DOI: 10.14744/nci.2017.26121
Is there any relationship between low PAPP-A levels and measures of umbilical vein and placental thickness during first trimester of pregnancy?
Abstract
Objective: Low pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A) level is associated with adverse perinatal outcomes. The purpose of this study was to evaluate relationship between umbilical cord diameter (UCD), umbilical vein and artery diameters (UVD, UAD), placental thickness, and PAPP-A level at gestational age of between 11 and 14 weeks.
Methods: UCD, UVD, UAD, and placental thickness of 246 women were assessed during ultrasound examination at between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation, as well as measurement of nuchal translucency (NT) and crown-rump length (CRL). Patients were divided into 2 groups according to PAPP-A percentile. Group 1 comprised 23 patients who had low PAPP-A (<0.44 multiple of medians [MoM], <10th percentile) and Group 2 was made up of 223 patients with PAPP-A of >0.44 MoM, >10th percentile. Calipers used for measurement were placed inner edge to inner edge of echogenic boundaries of the vessel. Largest sections of all vessels (UV and both arteries) were evaluated. Thickest part of the placenta was used for placental thickness measurement.
Results: Narrow UCD (<4.5±0.6 mm) was associated with low PAPP-A level (p=0.02). There was no significant difference in UVD, UAD, or placental thickness between groups. There was no significant difference in gestational age, CRL, or NT between groups. Fetal birth weight was significantly lower in Group 1 (p=0.03).
Conclusion: Closer attention to women with low-risk, healthy pregnancies and low PAPP-A level in first trimester screening results is recommended. They should be routinely screened for background medical risk factors and umbilical cord morphology in first trimester scan.
Keywords: First trimester; placental thickness; pregnancy-associated plasma protein A; umbilical cord; umbilical vein.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Screening for trisomy at 11-13 weeks' gestation: use of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, placental growth factor or both.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Sep;56(3):408-415. doi: 10.1002/uog.22140. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 32621353
-
First-trimester maternal serum level of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A is an independent predictor of fetal maxillary bone length.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2006 Jan;27(1):9-12. doi: 10.1002/uog.2671. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2006. PMID: 16374753
-
Routine first-trimester combined screening for pre-eclampsia: pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A or placental growth factor?Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Oct;58(4):540-545. doi: 10.1002/uog.23669. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33998078
-
Obstetrical complications associated with abnormal maternal serum markers analytes.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2008 Oct;30(10):918-932. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(16)32973-5. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2008. PMID: 19038077 Review. English, French.
-
First-trimester ultrasound and biochemical markers of aneuploidy and the prediction of impending fetal death.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2006 Oct;28(5):637-43. doi: 10.1002/uog.3809. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2006. PMID: 16952214 Review.
References
-
- Wu MH, Chang FM, Shen MR, Yao BL, Chang CH, Yu CH, et al. Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of single umbilical artery. J Clin Ultrasound. 1997;25:425–30. - PubMed
-
- Ghezzi F, Raio L, Di Naro E, Franchi M, Brühwiler H, D’Addario V, et al. First-trimester sonographic umbilical cord diameter and the growth of the human embryo. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001;18:348–51. - PubMed
-
- Weissman A, Jakobi P. Sonographic measurements of the umbilical cord in pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes. J Ultrasound Med. 1997;16:691–4. - PubMed
-
- Raio L, Ghezzi F, Di Naro E, Franchi M, Maymon E, Mueller MD, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of a lean umbilical cord:a simple marker for the fetus at risk of being small for gestational age at birth. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1999;13:176–80. - PubMed
-
- Bruch JF, Sibony O, Benali K, Challier JC, Blot P, Nessmann C. Computerized microscope morphometry of umbilical vessels from pregnancies with intrauterine growth retardation and abnormal umbilical artery Doppler. Hum Pathol. 1997;28:1139–45. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous