MicroRNAs in Atrial Fibrillation: from Expression Signatures to Functional Implications
- PMID: 28752208
- PMCID: PMC5550535
- DOI: 10.1007/s10557-017-6736-z
MicroRNAs in Atrial Fibrillation: from Expression Signatures to Functional Implications
Abstract
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained arrhythmia and is associated with pronounced morbidity and mortality. Its prevalence, expected to further increase for the forthcoming years, and associated frequent hospitalizations turn AF into a major health problem. Structural and electrical atrial remodelling underlie the substrate for AF, but the exact mechanisms driving this remodelling remain incompletely understood. Recent studies have shown that microRNAs (miRNA), short non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression, may be involved in the pathophysiology of AF. MiRNAs have been implicated in AF-induced ion channel remodelling and fibrosis. MiRNAs could therefore provide insight into AF pathophysiology or become novel targets for therapy with miRNA mimics or anti-miRNAs. Moreover, circulating miRNAs have been suggested as a new class of diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of AF. However, the origin and function of miRNAs in tissue and plasma frequently remain unknown and studies investigating the role of miRNAs in AF vary in design and focus and even present contradicting results. Here, we provide a systematic review of the available clinical and functional studies investigating the tissue and plasma miRNAs in AF and will thereafter discuss the potential of miRNAs as biomarkers or novel therapeutic targets in AF.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Electrical remodelling; Fibrosis; Therapy; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
J.R. de Groot received a grant from NWO/ZonMW(106.146.310). A.J. Tijsen received a grant from NWO/ZonMW(016.166.150). To the best of our knowledge, no conflict of interest, financial or other, exists for the co-authors. This article does not contain any original studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. There were no human cases included and thus no informed consent was needed.
Figures
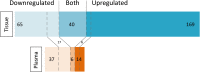
References
-
- Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, et al. 2016 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS: the task force for the management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)developed with the special contribution of the Europea. Eur Heart J 2016;:ehw210.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

