Ablative Radiotherapy as a Noninvasive Alternative to Catheter Ablation for Cardiac Arrhythmias
- PMID: 28752279
- PMCID: PMC5532420
- DOI: 10.1007/s11886-017-0886-2
Ablative Radiotherapy as a Noninvasive Alternative to Catheter Ablation for Cardiac Arrhythmias
Abstract
Purpose of review: Stereotactic radioablation is a commonly utilized technology to noninvasively treat solid tumors with precision and efficacy. Using a robotic arm mounted delivery system, multiple low-dose ionizing radiation beams are delivered from multiple angles, concentrating ablative energy at the target tissue. Recently, this technology has been evaluated for treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. This review will present the basic underlying principles, proof-of-principle studies, and clinical experience with stereotactic arrhythmia radioablation.
Recent findings: Most recently, stereotactic radioablation has been used to safely and effectively treat a limited number of patients with malignant arrhythmias, including ventricular tachycardia (VT) and atrial fibrillation (AF). Treatment protocols, outcomes, ongoing studies, and future directions will be discussed. Stereotactic radioablation is a well-established technology that has been shown to be a safe and effective therapy for patients with drug-refractory cardiac arrhythmias, including VT and AF. Further clinical evaluation to define safety and efficacy in larger populations of patients is needed.
Keywords: Ablation; Atrial fibrillation; Noninvasive; Radiosurgery; Stereotactic; Ventricular tachycardia.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
Paul C. Zei has received research support from Cyberheart, Inc.
Scott Soltys is a consultant for Nektar Therapeutics.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
All reported studies/experiments with human or animal subjects performed by the authors have been previously published and complied with all applicable ethical standards (including the Helsinki declaration and its amendments, institutional/national research committee standards, and international/national/institutional guidelines).
Figures
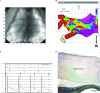
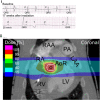
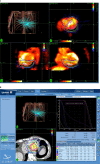
References
-
- Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Casadei B, Castella M, Diener HC, Heidbuchel H, Hendriks J, Hindricks G, Manolis AS, Oldgren J, Popescu BA, Schotten U, Van Putte B, Vardas P, Agewall S, Camm J, Esquivias GB, Budts W, Carerj S, Casselman P, Coca A, De Caterina R, Deftereos S, Dobrev D, Ferro JM, Filippatos G, Fitzsimons D, Gorenek B, Guenoun M, Hohnloser SH, Kolh P, Lip GYH, Manolis A, McMurray J, Ponikowski P, Rosenhek R, Ruschitzka F, Savelieva I, Sharma S, Suwalski P, Tamargo JL, Taylor CJ, Van Gelder IC, Voors AA, Windecker S, Zamorano JL, Zeppenfeld K. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Europace. 2016;18(11):1609–1678. doi: 10.1093/europace/euw295. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

