Ploidy Variation in Fungi: Polyploidy, Aneuploidy, and Genome Evolution
- PMID: 28752816
- PMCID: PMC5656283
- DOI: 10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0051-2016
Ploidy Variation in Fungi: Polyploidy, Aneuploidy, and Genome Evolution
Abstract
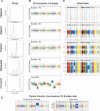
The ability of an organism to replicate and segregate its genome with high fidelity is vital to its survival and for the production of future generations. Errors in either of these steps (replication or segregation) can lead to a change in ploidy or chromosome number. While these drastic genome changes can be detrimental to the organism, resulting in decreased fitness, they can also provide increased fitness during periods of stress. A change in ploidy or chromosome number can fundamentally change how a cell senses and responds to its environment. Here, we discuss current ideas in fungal biology that illuminate how eukaryotic genome size variation can impact the organism at a cellular and evolutionary level. One of the most fascinating observations from the past 2 decades of research is that some fungi have evolved the ability to tolerate large genome size changes and generate vast genomic heterogeneity without undergoing canonical meiosis.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

