The Antitumor Activity of IMGN529, a CD37-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate, Is Potentiated by Rituximab in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Models
- PMID: 28753442
- PMCID: PMC5540712
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.06.001
The Antitumor Activity of IMGN529, a CD37-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate, Is Potentiated by Rituximab in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Models
Abstract
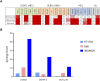
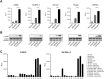
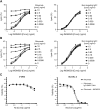
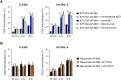
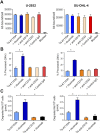
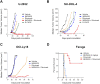
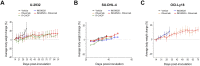
Naratuximab emtansine (IMGN529) is an investigational antibody-drug conjugate consisting of a CD37-targeting antibody conjugated to the maytansine-derived microtuble disruptor, DM1. IMGN529 has shown promising preclinical and clinical activity in non-Hodgkin lymphoma, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Due to the aggressive nature of the disease, DLBCL is often treated with combination therapies to maximize clinical outcomes; therefore, we investigated the potential of combining IMGN529 with both standard-of-care and emerging therapies against multiple oncology-relevant targets and pathways. The strongest enhancement in potency was seen with anti-CD20 antibodies, including rituximab. The combination of IMGN529 and rituximab was more potent than either agent alone, and this combinatorial benefit was associated with increased apoptotic induction and cell death. Additional studies revealed that rituximab treatment increased the internalization and degradation of the CD37-targeting antibody moiety of IMGN529. The combination of IMGN529 and rituximab was highly efficacious in multiple xenograft models, with superior antitumor efficacy seen compared to either agent alone or treatment with R-CHOP therapy. These findings suggest a novel mechanism whereby the potency of IMGN529 can be enhanced by CD20 binding, which results in the increased internalization and degradation of IMGN529 leading to the generation of greater amounts of cytotoxic catabolite. Overall, these data provide a biological rationale for the enhanced activity of IMGN529 in combination with rituximab and support the ongoing clinical evaluation of IMGN529 in combination with rituximab in patients with relapsed and/or refractory DLBCL.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PI3Kδ activation, IL6 over-expression, and CD37 loss cause resistance to the targeting of CD37-positive lymphomas with the antibody-drug conjugate naratuximab emtansine.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 16:2023.11.14.566994. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.14.566994. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 38014209 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A novel anti-CD37 antibody-drug conjugate with multiple anti-tumor mechanisms for the treatment of B-cell malignancies.Blood. 2013 Nov 14;122(20):3500-10. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-05-505685. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Blood. 2013. PMID: 24002446
-
The CD37-targeted antibody-drug conjugate IMGN529 is highly active against human CLL and in a novel CD37 transgenic murine leukemia model.Leukemia. 2014 Jul;28(7):1501-10. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.32. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Leukemia. 2014. PMID: 24445867 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Integration of Antibody-Drug Conjugate in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.Curr Oncol Rep. 2015 Sep;17(9):41. doi: 10.1007/s11912-015-0466-9. Curr Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26194424 Review.
-
SAR3419: an anti-CD19-Maytansinoid Immunoconjugate for the treatment of B-cell malignancies.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Oct 15;17(20):6448-58. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0485. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22003072 Review.
Cited by
-
CD20 and CD37 antibodies synergize to activate complement by Fc-mediated clustering.Haematologica. 2019 Sep;104(9):1841-1852. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.207266. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 30792198 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-Drug Conjugates: Possibilities and Challenges.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2019 Jan-Mar;11(1):3-23. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30800238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The novel CD19-targeting antibody-drug conjugate huB4-DGN462 shows improved anti-tumor activity compared to SAR3419 in CD19-positive lymphoma and leukemia models.Haematologica. 2019 Aug;104(8):1633-1639. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.211011. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 30733273 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor Immunity Is Controlled by Tetraspanin Proteins.Front Immunol. 2018 May 29;9:1185. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01185. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29896201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Past, Present, and Future of Rituximab-The World's First Oncology Monoclonal Antibody Therapy.Front Oncol. 2018 Jun 4;8:163. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00163. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29915719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ku M, Chong G, Hawkes EA. Tumour cell surface antigen targeted therapies in B-cell lymphomas: beyond rituximab. Blood Rev. 2017;31:23–25. - PubMed
-
- Maloney DG. Anti-CD20 antibody therapy for B-cell lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2008–2016. - PubMed
-
- van Spriel AB, Puls KL, Sofi M, Pouniotis D, Hochrein H, Orinska Z, Knobeloch KP, Plebanski M, Wright MD. A regulatory role for CD37 in T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 2004;172:2953–2961. - PubMed
-
- Link MP, Bindl J, Meeker TC, Carswell C, Doss CA, Warnke RA, Levy R. A unique antigen on mature B cells defined by a monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1986;137:3013–3018. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

