The Impact of Plasmacytoid Variant Histology on the Survival of Patients with Urothelial Carcinoma of Bladder after Radical Cystectomy
- PMID: 28753857
- PMCID: PMC6485953
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euf.2017.06.013
The Impact of Plasmacytoid Variant Histology on the Survival of Patients with Urothelial Carcinoma of Bladder after Radical Cystectomy
Abstract
Background: The clinical significance of the plasmacytoid variant (PCV) in urothelial carcinoma (UC) is currently lacking.
Objective: To compare clinical outcomes of patients with any PCV with that of patients with pure UC treated with radical cystectomy (RC).
Design, setting, and participants: We identified 98 patients who had pathologically confirmed PCV UC and 1312 patients with pure UC and no variant history who underwent RC at our institution between 1995 and 2014.
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Univariable and multivariable Cox regression and Cox proportional hazards regression to determine if PCV was associated with overall survival (OS).
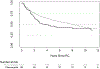
Results and limitations: Patients with PCV UC were more likely to have advanced tumor stage (p=0.001), positive lymph nodes (p=0.038), and receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy than those with pure UC (46% vs 22%, p<0.0001). The rate of positive soft tissue surgical margins was over five times greater in the PCV UC group compared with the pure UC group (21% vs 4.1%, respectively, p<0.0001). Median OS for the pure UC versus the PCV patients were 8 yr and 3.8 yr, respectively. On univariable analysis, PCV was associated with an increased risk of overall mortality (hazard ratio=1.34, 95% confidence interval: 1.02-1.78, p=0.039). However, on multivariable analysis adjusted for age, sex, neoadjuvant chemotherapy received, lymph node status, pathologic stage, and soft margin status, the association between PCV and OS was no longer significant (hazard ratio=1.06, 95% confidence interval: 0.78, 1.43, p=0.7). This retrospective study is limited by the lack of pathological reanalysis, and the impact of other concurrent mixed histology cannot be determined in this study.
Conclusions: Patients with PCV features have a higher disease burden at RC compared with those with pure UC. However, PCV was not an independent predictor of survival after RC on multivariable analysis, suggesting that PCV histology should not be used as an independent prognostic factor.
Patient summary: Plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma is a rare and aggressive form of bladder cancer. Patients with plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma had worse adverse pathologic features, but this was not associated with worse overall mortality when compared with patients with pure urothelial carcinoma.
Keywords: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy; Overall survival; Plasmacytoid variant; Radical cystectomy; Urothelial carcinoma of bladder.
Copyright © 2017 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, et al. The 2016 who classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part A: renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol 2016;70:93–105. - PubMed
-
- Kaimakliotis HZ, Monn MF, Cary KC, et al. Plasmacytoid variant urothelial bladder cancer: Is it time to update the treatment paradigm? Urol Oncol 2014;32:833–8. - PubMed
-
- Porten SP, Willis D, Kamat AM. Variant histology: Role in management and prognosis of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer. Curr Opin Urol 2014;24:517–23. - PubMed
-
- Xylinas E, Rink M, Robinson BD, et al. Impact of histological variants on oncological outcomes of patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder treated with radical cystectomy. Eur J Cancer 2013;49:1889–97. - PubMed
-
- Monn MF, Kaimakliotis HZ, Pedrosa JA, et al. Contemporary bladder cancer: variant histology may be a significant driver of disease. Urol Oncol 2015;33:18 e15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical