Amperometric Microsensors Monitoring Glutamate-Evoked In Situ Responses of Nitric Oxide and Carbon Monoxide from Live Human Neuroblastoma Cells
- PMID: 28753952
- PMCID: PMC5539859
- DOI: 10.3390/s17071661
Amperometric Microsensors Monitoring Glutamate-Evoked In Situ Responses of Nitric Oxide and Carbon Monoxide from Live Human Neuroblastoma Cells
Abstract
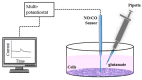
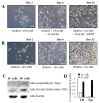
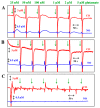
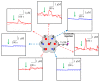
In the brain, nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide (CO) are important signaling gases which have multifaceted roles, such as neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, and vasodilators. Even though it is difficult to measure NO and CO in a living system due to their high diffusibility and extremely low release levels, electrochemical sensors are promising tools to measure in vivo and in vitro NO and CO gases. In this paper, using amperometric dual and septuple NO/CO microsensors, real-time NO and CO changes evoked by glutamate were monitored simultaneously for human neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells. In cultures, the cells were differentiated and matured into functional neurons by retinoic acid and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. When glutamate was administrated to the cells, both NO and CO increases and subsequent decreases returning to the basal levels were observed with a dual NO/CO microsensor. In order to facilitate sensor's measurement, a flower-type septuple NO/CO microsensor was newly developed and confirmed in terms of the sensitivity and selectivity. The septuple microsensor was employed for the measurements of NO and CO changes as a function of distances from the position of glutamate injection. Our sensor measurements revealed that only functionally differentiated cells responded to glutamate and released NO and CO.
Keywords: amperometric sensor; carbon monoxide; glutamate stimulation; neuroblastoma cells; nitric oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bidmon H.-J., Emde B., Oermann E., Kubitz R., Witte O.W., Zilles K. Heme oxygenase-1 (HSP-32) and heme oxygenase-2 induction in neurons and glial cells of cerebral regions and its relation to iron accumulation after focal cortical photothrombosis. Exp. Neurol. 2001;16:1–22. doi: 10.1006/exnr.2000.7456. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

