Sensitization of ASIC3 by proteinase-activated receptor 2 signaling contributes to acidosis-induced nociception
- PMID: 28754162
- PMCID: PMC5534107
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-017-0916-4
Sensitization of ASIC3 by proteinase-activated receptor 2 signaling contributes to acidosis-induced nociception
Abstract
Background: Tissue acidosis and inflammatory mediators play critical roles in pain. Pro-inflammatory agents trypsin and tryptase cleave and activate proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) expressed on sensory nerves, which is involved in peripheral mechanisms of inflammation and pain. Extracellular acidosis activates acid-sensing ion channel 3 (ASIC3) to trigger pain sensation. Here, we show that a functional interaction of PAR2 and ASIC3 could contribute to acidosis-induced nociception.
Methods: Electrophysiological experiments were performed on both rat DRG neurons and Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing ASIC3 and PAR2. Nociceptive behavior was induced by acetic acid in rats.
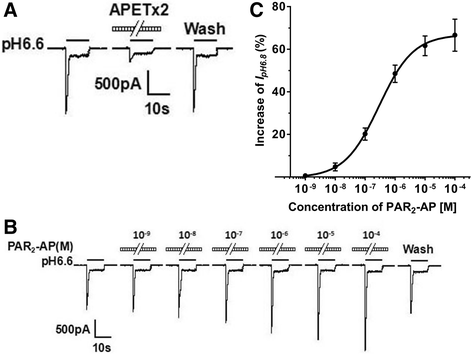
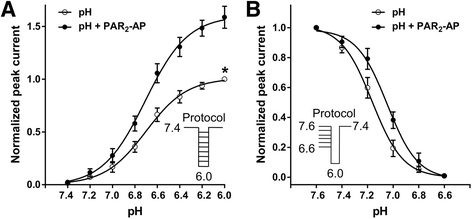
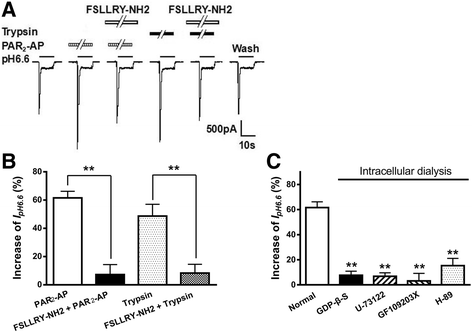
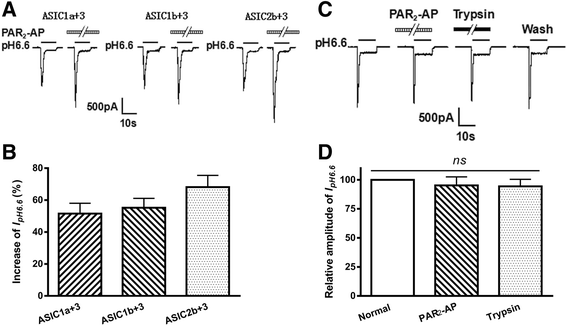
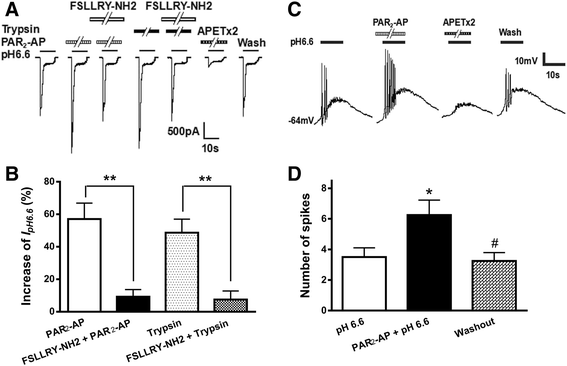
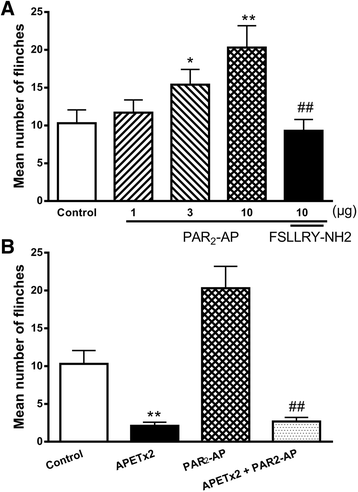
Results: PAR2-AP, PAR2-activating peptide, concentration-dependently increased the ASIC3 currents in CHO cells transfected with ASIC3 and PAR2. The proton concentration-response relationship was not changed, but that the maximal response increased 58.7 ± 3.8% after pretreatment of PAR2-AP. PAR2 mediated the potentiation of ASIC3 currents via an intracellular cascade. PAR2-AP potentiation of ASIC3 currents disappeared after inhibition of intracellular G protein, PLC, PKC, or PKA signaling. Moreover, PAR2 activation increased proton-evoked currents and spikes mediated by ASIC3 in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Finally, peripheral administration of PAR2-AP dose-dependently exacerbated acidosis-induced nocifensive behaviors in rats.
Conclusions: These results indicated that PAR2 signaling sensitized ASIC3, which may contribute to acidosis-induced nociception. These represent a novel peripheral mechanism underlying PAR2 involvement in hyperalgesia by sensitizing ASIC3 in primary sensory neurons.
Keywords: Acid-sensing ion channel 3; Dorsal root ganglion neuron; Nociception; Proteinase-activated receptor 2; Proton-gated current.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experimental protocol was approved by the animal research ethics committee of Hubei University of Science and Technology (No. 2016–67).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Hollenberg MD, Renaux B, Hyun E, Houle S, Vergnolle N, Saifeddine M, Ramachandran R. Derivatized 2-furoyl-LIGRLO-amide, a versatile and selective probe for proteinase-activated receptor 2: binding and visualization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;326:453–462. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.136432. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

