Residual atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in statin-treated adults: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 28754224
- PMCID: PMC6394854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacl.2017.06.015
Residual atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in statin-treated adults: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Abstract
Background: Residual atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk in statin-treated US adults without known ASCVD is not well described.
Objective: To quantitate residual ASCVD risk and its predictors in statin-treated adults.
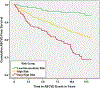
Methods: We studied 1014 statin-treated adults (53.3% female, mean 66.0 years) free of clinical ASCVD in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. We examined ASCVD event rates by National Lipid Association risk groups over 11-year follow-up and the relation of standard risk factors, biomarkers, and subclinical atherosclerosis measures with residual ASCVD event risk.
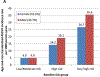
Results: Overall, 5.3% of participants were at low, 12.2% at moderate, 60.3% at high, and 22.2% at very high baseline risk. Despite statin therapy, age- and race-standardized ASCVD rates per 1000 person-years for men and women were both 4.9 for low/moderate risk, 19.1 and 14.2 for high risk, and 35.6 and 26.7 for very high risk, respectively. Specific independent predictors of residual risk included current smoking, family history, diabetes, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, low-density lipoprotein particle number, carotid intimal medial thickness, and especially coronary artery calcium score. Those on moderate- or high-intensity statins at baseline (compared with low intensity) had 39% lower risks and those who increased statin intensity 62% lower ASCVD event risks (P < .01).
Conclusion: Residual risk of ASCVD remains high despite statin treatment and is predicted by specific risk factors and subclinical atherosclerosis. These findings may be helpful for identifying those at highest risk needing more aggressive treatment.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular disease risk; Dyslipidemia; Risk factors; Statins.
Copyright © 2017 National Lipid Association. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Fruchart JC, Davignon J, Hermans MP, Al-Rubeaan K, Amarenco P, Assmann G, Barter P, Betteridge J, Bruckert E, Cuevas A, Farnier M, Ferrannini E, Fioretto P, Genest J, Ginsberg HN, Gotto AM Jr, Hu D, Kadowaki T, Kodama T, Krempf M,Matsuzawa Y, Núñez-Cortés JM, Monfil CC, Ogawa H, Plutzky J, Rader DJ, Sadikot S,Santos RD, Shlyakhto E, Sritara P, Sy R, Tall A, Tan CE, Tokgözoğlu L, Toth PP, Valensi P, Wanner C, Zambon A, Zhu J, Zimmet P; Residual Risk Reduction Initiative (R3i).. Residual macrovascular risk in 2013: what have we learned? Cardiovascular Diabetology 2014; 13: 26. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen GV, Parving HH, Pedersen O.. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348(5):383–93. - PubMed
-
- Wong ND, Patao C, Malik S, Kamath TV, L’Italien GJ, Pio JR, Williams R. Preventable Coronary Heart Disease Events from Control of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in US Adults with Diabetes (Projections from Utilizing the UKPDS Risk Engine). Am J Cardiol. 2014; 113(8):1356–61. - PubMed
-
- The Scanadinavian Simvastatin Survival Study Group. Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet 1994; 344(8934):1383–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

