A Modified Preserved Nasal and Lacrimal Flap Technique in Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy
- PMID: 28754905
- PMCID: PMC5533767
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-07364-9
A Modified Preserved Nasal and Lacrimal Flap Technique in Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy
Abstract
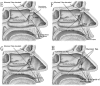
Here we describe a modified preserved nasal and lacrimal mucosal flap technique in endonasal endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy (EES-DCR) for patients with epiphora secondary to primary acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction (PANDO) and evaluate its outcomes. Twenty-five patients with PANDO were retrospectively reviewed. Modified preserved nasal and lacrimal mucosal flap technique in EES-DCR was applied in all 27 eyes of 25 patients. The patients were evaluated with objective (anatomical patency) and subjective (symptomatic cure) success rates within the duration of follow-up. In the present study, all of the patients' surgical procedures were successful. There were 2 cases of flap dislocation from the rhinostomy site 1 week post-operation. After a mean follow-up of 4.9 ± 1.8 months, the success rate of anatomical patency was 100% (27/27) and the success rate of symptomatic cure was 92.6% (25/27). No significant complications occurred intraoperatively. We concluded that the modified preserved nasal and lacrimal mucosal flap technique in EES-DCR for treating PANDO is simple and safe, can effectively cover the bare bone around the opened sac, and provide a similar or even better clinical outcome compared with other routine treatment techniques used for this condition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Toti A. Nuovo metodo conservatore di cura radicale delle suppurazioni croniche del sacco lacrimale (dacriocistorinostomia) Clin Mod Firenze. 1904;10:385–387.
-
- Zilelioglu G, et al. Results of endoscopic endonasal non-laser dacryocystorhinostomy. Documenta ophthalmologica. Advances in ophthalmology. 2002;105:57–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

