Oral exposure to arsenic causes hearing loss in young people aged 12-29 years and in young mice
- PMID: 28754998
- PMCID: PMC5533757
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-06096-0
Oral exposure to arsenic causes hearing loss in young people aged 12-29 years and in young mice
Abstract
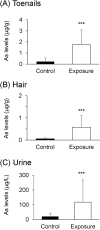
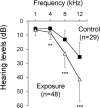
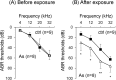
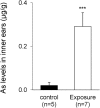
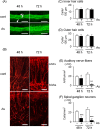
There is no information on the association between oral exposure to arsenic (As) and hearing loss in humans or mice. In this combined epidemiological study and experimental study, the association of oral exposure to As with hearing loss in people aged 12-29 years and young mice was examined. Subjects in the exposure group (n = 48), who were drinking tube well water contaminated with As, showed significantly higher risks of hearing loss at 4 kHz [odds ratio (OR) = 7.60; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.56, 57.88], 8 kHz (OR = 5.00; 95% CI: 1.48, 18.90) and 12 kHz (OR = 8.72; 95% CI: 2.09, 47.77) than did subjects in the control group (n = 29). We next performed an experiment in which young mice were exposed to As via drinking water at 22.5 mg/L, which is a much greater concentration than that in human studies. The exposure group showed hearing loss and accumulation of As in inner ears. Ex vivo exposure of the organ of Corti from mice exposed to As significantly decreased the number of auditory neurons and fibers. Thus, our combined study showed that oral exposure to As caused hearing loss in young people and young mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hearing loss in humans drinking tube well water with high levels of iron in arsenic-polluted area.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 21;9(1):9028. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45524-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31227759 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic level in toenails is associated with hearing loss in humans.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 5;13(7):e0198743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198743. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29975704 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between chronic exposure to arsenic through drinking water and hearing function in exposed population aged 10-49 years: A cross-sectional study.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021 Mar 15;211:111939. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111939. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021. PMID: 33476847
-
Effect of drinking arsenic-contaminated water in children.Indian J Public Health. 2012 Jul-Sep;56(3):223-6. doi: 10.4103/0019-557X.104250. Indian J Public Health. 2012. PMID: 23229215 Review.
-
Arsenicosis history and research progress in Mainland China.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2011 Sep;27(9):377-81. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2011.05.004. Epub 2011 Aug 23. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21914524 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated arsenic level in fasting serum via ingestion of fish meat increased the risk of hypertension in humans and mice.Eur Heart J Open. 2023 Sep 4;3(5):oead074. doi: 10.1093/ehjopen/oead074. eCollection 2023 Sep. Eur Heart J Open. 2023. PMID: 37671121 Free PMC article.
-
Association between urinary arsenic and hearing threshold shifts in adults in the United States, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2015-2016.Front Public Health. 2024 Dec 18;12:1431122. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1431122. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39744375 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Symptoms, Neurological Signs, and Electrophysiological Findings in Surviving Residents with Probable Arsenic Exposure in Toroku, Japan.Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2018 Nov;75(4):521-529. doi: 10.1007/s00244-018-0544-8. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29974180 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of balance in young adults by a sound component at 100 Hz in music.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 15;8(1):16894. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35244-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30442994 Free PMC article.
-
Hearing loss in humans drinking tube well water with high levels of iron in arsenic-polluted area.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 21;9(1):9028. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45524-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31227759 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

