Adolescent stress leads to glutamatergic disturbance through dopaminergic abnormalities in the prefrontal cortex of genetically vulnerable mice
- PMID: 28756461
- PMCID: PMC8034555
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-017-4704-8
Adolescent stress leads to glutamatergic disturbance through dopaminergic abnormalities in the prefrontal cortex of genetically vulnerable mice
Abstract
Background: Stress during the adolescent period influences postnatal maturation and behavioral patterns in adulthood. Adolescent stress-induced molecular and functional changes in neurons are the key clinical features of psychiatric disorders including schizophrenia.
Objective: In the present study, we exposed genetically vulnerable mice to isolation stress to examine the molecular changes in the glutamatergic system involving N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors via dopaminergic disturbance in the prefrontal cortex (PFc).
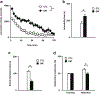
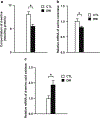
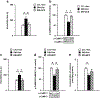
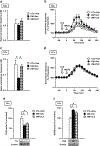
Results: We report that late adolescent stress in combination with Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) genetic risk elicited alterations in glutamatergic neurons in the PFc, such as increased expression of glutamate transporters, decreased extracellular levels of glutamate, decreased concentration of d-serine, and impaired activation of NMDA-Ca2+/calmodulin kinase II signaling. These changes resulted in behavioral deficits in locomotor activity, forced swim, social interaction, and novelty preference tests. The glutamatergic alterations in the PFc were prevented if the animals were treated with an atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine and a dopamine D1 agonist SKF81297, which suggests that the activation of dopaminergic neurons is involved in the regulation of the glutamatergic system.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that adolescent stress combined with dopaminergic abnormalities in the PFc of genetically vulnerable mice induces glutamatergic disturbances, which leads to behavioral deficits in the young adult stage.
Keywords: Adolescent stress; Dopaminergic neuron; Genetic vulnerability; Glutamatergic neuron; Prefrontal cortex.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Interaction of dopamine D1 and NMDA receptors mediates acute clozapine potentiation of glutamate EPSPs in rat prefrontal cortex.J Neurophysiol. 2002 May;87(5):2324-36. doi: 10.1152/jn.2002.87.5.2324. J Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11976371
-
Involvement of a dysfunctional dopamine-D1/N-methyl-d-aspartate-NR1 and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II pathway in the impairment of latent learning in a model of schizophrenia induced by phencyclidine.Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Jun;71(6):1598-609. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.032961. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Mol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17344353
-
Regulation of NMDA receptors by dopamine D4 signaling in prefrontal cortex.J Neurosci. 2003 Oct 29;23(30):9852-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-30-09852.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14586014 Free PMC article.
-
Animal model of schizophrenia: dysfunction of NMDA receptor-signaling in mice following withdrawal from repeated administration of phencyclidine.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Nov;1086:160-8. doi: 10.1196/annals.1377.003. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17185514 Review.
-
Unraveling monoamine receptors involved in the action of typical and atypical antipsychotics on glutamatergic and serotonergic transmission in prefrontal cortex.Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(5):502-15. doi: 10.2174/138161210790361416. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 19909228 Review.
Cited by
-
Hispidulin attenuates the social withdrawal in isolated disrupted-in-schizophrenia-1 mutant and chronic phencyclidine-treated mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Jul;177(14):3210-3224. doi: 10.1111/bph.15043. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32133633 Free PMC article.
-
Korean Red Ginseng and Rb1 restore altered social interaction, gene expressions in the medial prefrontal cortex, and gut metabolites under post-weaning social isolation in mice.J Ginseng Res. 2024 Sep;48(5):481-493. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2024.03.005. Epub 2024 Mar 25. J Ginseng Res. 2024. PMID: 39263309 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged HPA axis dysregulation in postpartum depression associated with adverse early life experiences: A cross-species translational study.Nat Ment Health. 2024 May;2(5):593-604. doi: 10.1038/s44220-024-00217-1. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Nat Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 38736646 Free PMC article.
-
Adolescent stress accelerates postpartum novelty recognition impairment in 5xFAD mice.Front Neurosci. 2024 May 15;18:1366199. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1366199. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38812977 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic, long-term effects of glutamate dehydrogenase 1 deficiency and mild stress on cognitive function and mPFC gene and miRNA expression.Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Jul 7;13(1):248. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02534-y. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37419882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abazyan B, Dziedzic J, Hua K, Abazyan S, Yang C, Mori S, Pletnikov MV, Guilarte TR (2014) Chronic exposure of mutant DISC1 mice to lead produces sex-dependent abnormalities consistent with schizophrenia and related mental disorders: a gene-environment interaction study. Schizophr Bull 40:575–584 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aoyama Y, Mouri A, Toriumi K, Koseki T, Narusawa S, Ikawa N, Mamiya T, Nagai T, Yamada K, Nabeshima T (2014) Clozapine ameliorates epigenetic and behavioral abnormalities induced by phencyclidine through activation of dopamine D1 receptor. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17:723–737 - PubMed
-
- Axelrod J, Reisine TD (1984) Stress hormones: their interaction and regulation. Science 224:452–459 - PubMed
-
- Ayhan Y, Abazyan B, Nomura J, Kim R, Ladenheim B, Krasnova IN, Sawa A, Margolis RL, Cadet JL, Mori S, Vogel MW, Ross CA, Pletnikov MV (2011) Differential effects of prenatal and postnatal expressions of mutant human DISC1 on neurobehavioral phenotypes in transgenic mice: evidence for neurodevelopmental origin of major psychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry 16:293–306 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

