Converging Prefronto-Insula-Amygdala Pathways in Negative Emotion Regulation in Marmoset Monkeys
- PMID: 28756869
- PMCID: PMC5697497
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.06.016
Converging Prefronto-Insula-Amygdala Pathways in Negative Emotion Regulation in Marmoset Monkeys
Abstract
Background: Impaired regulation of emotional responses to potential threat is a core feature of affective disorders. However, while the subcortical circuitry responsible for processing and expression of fear has been well characterized, the top-down control of this circuitry is less well understood. Our recent studies demonstrated that heightened emotionality, as measured both physiologically and behaviorally, during conditioned fear and innate/social threat was induced, independently, by excitotoxic lesions of either the anterior orbitofrontal cortex (antOFC) or ventrolateral prefrontal cortex (vlPFC). An important outstanding question is whether the antOFC and vlPFC act on common or distinct downstream targets to regulate negative emotion.
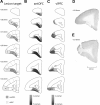
Methods: The question was addressed by combining localized excitotoxic lesions in the PFC of a nonhuman primate and functional neuroimaging ([18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography) with a fear-regulating extinction paradigm. Marmoset monkeys with unilateral lesions of either the antOFC or vlPFC were scanned immediately following exposure to a fearful or safe context, and differences in [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake were evaluated.
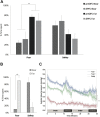
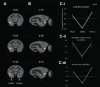
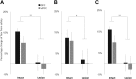
Results: [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the insula and amygdala of the intact hemisphere was significantly increased in response to the fearful context compared with the safe context. Such discrimination between the two contexts was not reflected in the activity of the insula-amygdala of the antOFC or vlPFC-lesioned hemisphere. Instead, uptake was at an intermediate level in both contexts.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate that the distinct control functions of the antOFC and vlPFC converge on the same downstream targets to promote emotion regulation, taking us closer to a mechanistic understanding of different forms of anxiety.
Keywords: Amygdala; Emotion regulation; Insula; Orbitofrontal cortex; Prefrontal cortex; Ventrolateral prefrontal cortex.
Copyright © 2017 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lesions of ventrolateral prefrontal or anterior orbitofrontal cortex in primates heighten negative emotion.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Aug 15;72(4):266-72. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.03.007. Epub 2012 Apr 12. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22502990
-
Lesions of either anterior orbitofrontal cortex or ventrolateral prefrontal cortex in marmoset monkeys heighten innate fear and attenuate active coping behaviors to predator threat.Front Syst Neurosci. 2015 Jan 21;8:250. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2014.00250. eCollection 2014. Front Syst Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25653599 Free PMC article.
-
Trait Anxiety Mediated by Amygdala Serotonin Transporter in the Common Marmoset.J Neurosci. 2020 Jun 10;40(24):4739-4749. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2930-19.2020. Epub 2020 May 11. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32393533 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Circuitry of Impaired Emotion Regulation in Substance Use Disorders.Am J Psychiatry. 2016 Apr 1;173(4):344-61. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15060710. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Am J Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26771738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired emotional learning and involvement of the corticotropin-releasing factor signaling system in patients with irritable bowel syndrome.Gastroenterology. 2013 Dec;145(6):1253-61.e1-3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.016. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23954313 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebral blood flow in 5- to 8-month-olds: Regional tissue maturity is associated with infant affect.Dev Sci. 2020 Sep;23(5):e12928. doi: 10.1111/desc.12928. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Dev Sci. 2020. PMID: 31802580 Free PMC article.
-
The central extended amygdala in fear and anxiety: Closing the gap between mechanistic and neuroimaging research.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Feb 6;693:58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.11.056. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 29195911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disturbed effective connectivity patterns in an intrinsic triple network model are associated with posttraumatic stress disorder.Neurol Sci. 2019 Feb;40(2):339-349. doi: 10.1007/s10072-018-3638-1. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30448966
-
Combining brain perturbation and neuroimaging in non-human primates.Neuroimage. 2021 Jul 15;235:118017. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118017. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 33794355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expected value and sensitivity to punishment modulate insular cortex activity during risky decision making.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 17;10(1):11920. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68644-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32681146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patel V., Chisholm D., Parikh R., Charlson F.J., Degenhardt L., Dua T. Addressing the burden of mental, neurological, and substance use disorders: Key messages from Disease Control Priorities, 3rd edition. Lancet. 2016;387:1672–1685. - PubMed
-
- Bystritsky A. Treatment-resistant anxiety disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2006;11:805–814. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

