An Efficient Platform for Astrocyte Differentiation from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 28757165
- PMCID: PMC5550034
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.06.018
An Efficient Platform for Astrocyte Differentiation from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
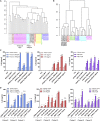
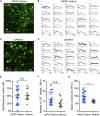
Growing evidence implicates the importance of glia, particularly astrocytes, in neurological and psychiatric diseases. Here, we describe a rapid and robust method for the differentiation of highly pure populations of replicative astrocytes from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs), via a neural progenitor cell (NPC) intermediate. We evaluated this protocol across 42 NPC lines (derived from 30 individuals). Transcriptomic analysis demonstrated that hiPSC-astrocytes from four individuals are highly similar to primary human fetal astrocytes and characteristic of a non-reactive state. hiPSC-astrocytes respond to inflammatory stimulants, display phagocytic capacity, and enhance microglial phagocytosis. hiPSC-astrocytes also possess spontaneous calcium transient activity. Our protocol is a reproducible, straightforward (single medium), and rapid (<30 days) method to generate populations of hiPSC-astrocytes that can be used for neuron-astrocyte and microglia-astrocyte co-cultures for the study of neuropsychiatric disorders.
Keywords: astrocyte; human induced pluripotent stem cell; iPSC.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Barres B.A. The mystery and magic of glia: a perspective on their roles in health and disease. Neuron. 2008;60:430–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

