Enhancer Reprogramming Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis
- PMID: 28757253
- PMCID: PMC5726277
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.007
Enhancer Reprogramming Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis
Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) is one of the most lethal human malignancies, owing in part to its propensity for metastasis. Here, we used an organoid culture system to investigate how transcription and the enhancer landscape become altered during discrete stages of disease progression in a PDA mouse model. This approach revealed that the metastatic transition is accompanied by massive and recurrent alterations in enhancer activity. We implicate the pioneer factor FOXA1 as a driver of enhancer activation in this system, a mechanism that renders PDA cells more invasive and less anchorage-dependent for growth in vitro, as well as more metastatic in vivo. In this context, FOXA1-dependent enhancer reprogramming activates a transcriptional program of embryonic foregut endoderm. Collectively, our study implicates enhancer reprogramming, FOXA1 upregulation, and a retrograde developmental transition in PDA metastasis.
Keywords: FOXA1; enhancer; metastasis; organoid; pancreatic cancer; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
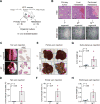

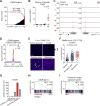
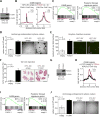

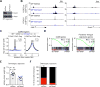
Comment in
-
Reprogramming Enhancers to Drive Metastasis.Cell. 2017 Aug 24;170(5):823-825. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.08.010. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28841414
References
-
- Bailey P, Chang DK, Nones K, Johns AL, Patch AM, Gingras MC, Miller DK, Christ AN, Bruxner TJ, Quinn MC, et al. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2016;531:47–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20 CA192996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA093373/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA188134/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA190092/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R50 CA211506/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA101955/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180944/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA045508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA013106/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK089502/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 CA192994/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA127297/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R50 CA211462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA126607/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA168409/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA180717/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

