Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Commonly Used Fruits and Vegetables in Kuwait
- PMID: 28757570
- PMCID: PMC5580537
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph14080833
Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Commonly Used Fruits and Vegetables in Kuwait
Abstract
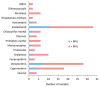
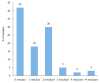
The presence of pesticide residues in primary and derived agricultural products raises serious health concerns for consumers. The aim of this study was to assess the level of pesticide residues in commonly consumed fruits and vegetables in Kuwait. A total of 150 samples of different fresh vegetables and fruits were analyzed for the presence of 34 pesticides using the quick easy cheap effective rugged and safe (QuEChERS) multi-residue extraction, followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Pesticide residues above the maximum residue limits (MRL) were detected in 21% of the samples and 79% of the samples had no residues of the pesticides surveyed or contained residues below the MRL. Multiple residues were present in 40% of the samples with two to four pesticides, and four samples were contaminated with more than four pesticide residues. Of the pesticides investigated, 16 were detected, of which imidacloprid, deltamethrin, cypermethrin, malathion, acetamiprid, monocrotophos, chlorpyrifos-methyl, and diazinon exceeded their MRLs. Aldrin, an organochlorine pesticide, was detected in one apple sample, with residues below the MRL. The results indicate the occurrence of pesticide residues in commonly consumed fruits and vegetables in Kuwait, and pointed to an urgent need to develop comprehensive intervention measures to reduce the potential health risk to consumers. The need for the regular monitoring of pesticide residues and the sensitization of farmers to better pesticide safety practices, especially the need to adhere to recommended pre-harvest intervals is recommended.
Keywords: GC-MS; Kuwait; LC-MS/MS; food safety; fruits; pesticide residues; vegetables.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsor had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables from the Aegean region, Turkey.Food Chem. 2014 Oct 1;160:379-92. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.051. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24799252
-
LC-MS/MS determination of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables.J Environ Sci Health B. 2017 Jul 3;52(7):446-457. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2017.1301755. Epub 2017 Mar 29. J Environ Sci Health B. 2017. PMID: 28353394
-
Levels of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables in the Turkish domestic markets.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Aug;28(29):39451-39457. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13538-w. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33759100
-
Recent Modifications and Validation of QuEChERS-dSPE Coupled to LC-MS and GC-MS Instruments for Determination of Pesticide/Agrochemical Residues in Fruits and Vegetables: Review.J Chromatogr Sci. 2018 Aug 1;56(7):656-669. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmy032. J Chromatogr Sci. 2018. PMID: 29688338 Review.
-
Assessment of residues from common pesticides and associated risks in Pakistan.Environ Monit Assess. 2024 Oct 16;196(11):1061. doi: 10.1007/s10661-024-13220-x. Environ Monit Assess. 2024. PMID: 39414624 Review.
Cited by
-
Pesticide residues in tomato and tomato products marketed in Majmaah province, KSA, and their impact on human health.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Mar;27(8):8526-8534. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07573-x. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31907808
-
Study on the Dynamic Difference between Single and Mixed Residues of Three Neonicotinoids in Brassica chinensis L.Molecules. 2021 Oct 27;26(21):6495. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216495. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770902 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of imidacloprid residues in mango, cowpea and water samples based on portable molecular imprinting sensors.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 2;16(9):e0257042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257042. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34473806 Free PMC article.
-
Residues of Deltamethrin in Pine Needles and Pine Nuts of Catalonia (Spain).Molecules. 2023 Dec 12;28(24):8050. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248050. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138540 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus cereus MH778713 elicits tomato plant protection against Fusarium oxysporum.J Appl Microbiol. 2022 Jan;132(1):470-482. doi: 10.1111/jam.15179. Epub 2021 Jul 6. J Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34137137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pimentel D. Environmental and economic cost of the application of pesticides primarily in the United States. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2005;7:229–252. doi: 10.1007/s10668-005-7314-2. - DOI
-
- Jeyaratnam J. Acute pesticide poisoning: A major global health problem. World Health Stat. Q. 1990;43:139–144. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous