Finding a Balance between Protection and Pathology: The Dual Role of Perforin in Human Disease
- PMID: 28757574
- PMCID: PMC5578000
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18081608
Finding a Balance between Protection and Pathology: The Dual Role of Perforin in Human Disease
Abstract
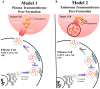
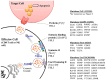
Perforin is critical for controlling viral infection and tumor surveillance. Clinically, mutations in perforin are viewed as unfavorable, as lack of this pore-forming protein results in lethal, childhood disease, familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 2 (FHL 2). However, many mutations in the coding region of PRF1 are not yet associated with disease. Animal models of viral-associated blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption and experimental cerebral malaria (ECM) have identified perforin as critical for inducing pathologic central nervous system CNS vascular permeability. This review focuses on the role of perforin in both protecting and promoting human disease. It concludes with a novel hypothesis that diversity observed in the PRF1 gene may be an example of selective advantage that protects an individual from perforin-mediated pathology, such as BBB disruption.
Keywords: blood–brain barrier disruption; familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 2; perforin; selective advantage; single nucleotide variants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lopez J.A., Susanto O., Jenkins M.R., Lukoyanova N., Sutton V.R., Law R.H., Johnston A., Bird C.H., Bird P.I., Whisstock J.C., et al. Perforin forms transient pores on the target cell plasma membrane to facilitate rapid access of granzymes during killer cell attack. Blood. 2013;121:2659–2668. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-07-446146. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

