RORα controls hepatic lipid homeostasis via negative regulation of PPARγ transcriptional network
- PMID: 28757615
- PMCID: PMC5534431
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00215-1
RORα controls hepatic lipid homeostasis via negative regulation of PPARγ transcriptional network
Abstract
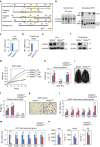
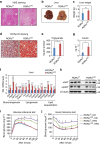
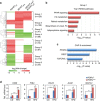
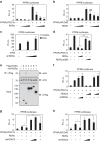
The retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor-α (RORα) is an important regulator of various biological processes, including cerebellum development, circadian rhythm and cancer. Here, we show that hepatic RORα controls lipid homeostasis by negatively regulating transcriptional activity of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) that mediates hepatic lipid metabolism. Liver-specific Rorα-deficient mice develop hepatic steatosis, obesity and insulin resistance when challenged with a high-fat diet (HFD). Global transcriptome analysis reveals that liver-specific deletion of Rorα leads to the dysregulation of PPARγ signaling and increases hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism. RORα specifically binds and recruits histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) to PPARγ target promoters for the transcriptional repression of PPARγ. PPARγ antagonism restores metabolic homeostasis in HFD-fed liver-specific Rorα deficient mice. Our data indicate that RORα has a pivotal role in the regulation of hepatic lipid homeostasis. Therapeutic strategies designed to modulate RORα activity may be beneficial for the treatment of metabolic disorders.Hepatic steatosis development may result from dysregulation of lipid metabolism, which is finely tuned by several transcription factors including the PPAR family. Here Kim et al. show that the nuclear receptor RORα inhibits PPARγ-mediated transcriptional activity by interacting with HDAC3 and competing for the promoters of lipogenic genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptional profiling reveals a role for RORalpha in regulating gene expression in obesity-associated inflammation and hepatic steatosis.Physiol Genomics. 2011 Jul 14;43(13):818-28. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00206.2010. Epub 2011 May 3. Physiol Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21540300 Free PMC article.
-
Liver-specific RORα deletion does not affect the metabolic susceptibility to western style diet feeding.Mol Metab. 2019 May;23:82-87. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30904385 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic fatty acid transporter Cd36 is a common target of LXR, PXR, and PPARgamma in promoting steatosis.Gastroenterology. 2008 Feb;134(2):556-67. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.11.037. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18242221
-
Dissecting the Rev-erbα Cistrome and the Mechanisms Controlling Circadian Transcription in Liver.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2015;80:233-8. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2015.80.027508. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2015. PMID: 26370410 Review.
-
Hepatic lipid accumulation: cause and consequence of dysregulated glucoregulatory hormones.J Endocrinol. 2017 Jul;234(1):R1-R21. doi: 10.1530/JOE-16-0513. Epub 2017 Apr 20. J Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28428362 Review.
Cited by
-
Nobiletin, a polymethoxylated flavonoid, regulates cell survival via the nuclear receptor RORα in cardiomyocytes.J Cardiovasc Aging. 2024 Jan;4(1):6. doi: 10.20517/jca.2023.46. Epub 2023 Dec 31. J Cardiovasc Aging. 2024. PMID: 39119356 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Targeting Liver Epsins Ameliorates Dyslipidemia in Atherosclerosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 27:2024.08.26.609742. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.26.609742. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39253478 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Narrative Review: Glucocorticoids in Alcoholic Hepatitis-Benefits, Side Effects, and Mechanisms.J Xenobiot. 2022 Sep 21;12(4):266-288. doi: 10.3390/jox12040019. J Xenobiot. 2022. PMID: 36278756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bifidobacterial carbohydrate/nucleoside metabolism enhances oxidative phosphorylation in white adipose tissue to protect against diet-induced obesity.Microbiome. 2022 Nov 4;10(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s40168-022-01374-0. Microbiome. 2022. PMID: 36333752 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted sequencing analysis of PPARG identifies a risk variant associated with obstructive sleep apnea in Chinese Han subjects.Sleep Breath. 2020 Mar;24(1):167-174. doi: 10.1007/s11325-019-01855-x. Epub 2019 May 2. Sleep Breath. 2020. PMID: 31044373 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

