Peripheral Exophytic Oral Lesions: A Clinical Decision Tree
- PMID: 28757870
- PMCID: PMC5516740
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9193831
Peripheral Exophytic Oral Lesions: A Clinical Decision Tree
Abstract
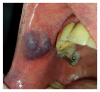
Diagnosis of peripheral oral exophytic lesions might be quite challenging. This review article aimed to introduce a decision tree for oral exophytic lesions according to their clinical features. General search engines and specialized databases including PubMed, PubMed Central, Medline Plus, EBSCO, Science Direct, Scopus, Embase, and authenticated textbooks were used to find relevant topics by means of keywords such as "oral soft tissue lesion," "oral tumor like lesion," "oral mucosal enlargement," and "oral exophytic lesion." Related English-language articles published since 1988 to 2016 in both medical and dental journals were appraised. Upon compilation of data, peripheral oral exophytic lesions were categorized into two major groups according to their surface texture: smooth (mesenchymal or nonsquamous epithelium-originated) and rough (squamous epithelium-originated). Lesions with smooth surface were also categorized into three subgroups according to their general frequency: reactive hyperplastic lesions/inflammatory hyperplasia, salivary gland lesions (nonneoplastic and neoplastic), and mesenchymal lesions (benign and malignant neoplasms). In addition, lesions with rough surface were summarized in six more common lesions. In total, 29 entities were organized in the form of a decision tree in order to help clinicians establish a logical diagnosis by a stepwise progression method.
Figures



















References
-
- Wood N. K., Goaz P. W. Differential Diagnosis of Oral And Maxillofacial Lesions. 5th Edition. St. Louis, Mo, USA: Mosby; 1997.
-
- Glick M. Burket's Oral Medicine. 12th edition. People's medical publishing house; 2015. 147-172, 175-188, 236-237.
-
- Bermejo-Fenoll A., López-Jornet P. Differential diagnosis of exophytic lesions of soft oral tissue. Medicina Oral, Patologia Oral y Cirugia Bucal. 2005;10(5):470–471. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

