Investigating the application of a nitroreductase-expressing transgenic zebrafish line for high-throughput toxicity testing
- PMID: 28758069
- PMCID: PMC5527975
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2017.04.005
Investigating the application of a nitroreductase-expressing transgenic zebrafish line for high-throughput toxicity testing
Abstract
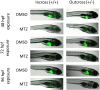
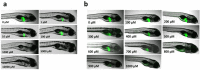
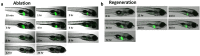
Nitroreductase enzymes are responsible for the reduction of nitro functional groups to amino functional groups, and are found in a range of animal models, zebrafish (Danio rerio) excluded. Transgenic zebrafish models have been developed for tissue-specific cell ablation, which use nitroreductase to ablate specific tissues or cell types following exposure to the non-toxic pro-drug metronidazole (MTZ). When metabolized by nitroreductase, MTZ produces a potent cytotoxin, which specifically ablates the tissue in which metabolism occurs. Uses, beyond tissue-specific cell ablation, are possible for the hepatocyte-specific Tg(l-fabp:CFP-NTR)s891 zebrafish line, including investigations of the role of nitroreductase in the toxicity of nitrated compounds. The hepatic ablation characteristics of this transgenic line were explored, in order to expand its potential uses. Embryos were exposed at 48, 72, or 96 hours post fertilization (hpf) to a range of MTZ concentrations, and the ablation profiles were compared. Ablation occurred at a 10-fold lower concentration than previously reported. Embryos were exposed to a selection of other compounds, with and without MTZ, in order to investigate alternative uses for this transgenic line. Test compounds were selected based on: their ability to undergo nitroreduction, known importance of hepatic metabolism to toxicity, and known pharmaceutical hepatotoxins. Selected compounds included nitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (nitro-PAHs), the PAHs retene and benzo[a]pyrene, and the pharmaceuticals acetaminophen and flutamide. The results suggest a range of potential roles of the liver in the toxicity of these compounds, and highlight the additional uses of this transgenic model in toxicity testing.
Keywords: nitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon; nitroreductase; pharmaceuticals; tissue ablation; transgenic; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
