Contrast Spread in the Superoposterior Approach of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections for Lumbosacral Radiculopathy
- PMID: 28758078
- PMCID: PMC5532346
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.3.413
Contrast Spread in the Superoposterior Approach of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections for Lumbosacral Radiculopathy
Abstract
Objective: To observe the contrast spread in superoposterior transforaminal epidural steroid injection (SP TFESI) and investigate the correlation between spread patterns and efficacy.
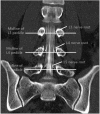
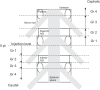
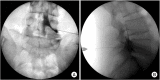
Methods: Thirty-one patients with lumbosacral radiculopathy underwent single-level TFESI under fluoroscopy. The final needle tip position was targeted toward the SP quadrant of the intervertebral foramen. To observe the spread, 1 mL of contrast material was injected, followed by a steroid injection. The contrast spread was graded anteroposteriorly and vertically in the epidural space. The effect of SP TFESI was evaluated by proportional pain score reduction.
Results: Levels injected were L4-5 (n=20) and L5-S1 (n=11). Seventeen cases were lateral, and 14 were central herniated disc (HD). Baseline mean visual analog scale score was 6.23. Contrast dispersed dorsally in all the cases, and 45.2% cases showed a concurrent ventral spread. The proportion of the pain reduction after 2 weeks showed no difference between the two groups. In vertical spreading analysis, mean cephalic/caudal grades were 1.40/1.55 at L4-5 level and 1.73/1.64 at L5-S1 level. The HD location had no effect on contrast dispersion.
Conclusion: In SP TFESI, ventral contrast spread did not guarantee a better effect; however, the extent of cephalic flow in ventral expansion group correlated with the proportion of pain reduction.
Keywords: Contrast media; Epidural injection; Lumbosacral; Radiculopathy; Treatment outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Manchikanti L, Staats PS, Singh V, Schultz DM, Vilims BD, Jasper JF, et al. Evidence-based practice guidelines for interventional techniques in the management of chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2003;6:3–81. - PubMed
-
- Boswell MV, Hansen HC, Trescot AM, Hirsch JA. Epidural steroids in the management of chronic spinal pain and radiculopathy. Pain Physician. 2003;6:319–334. - PubMed
-
- Ackerman WE, 3rd, Ahmad M. The efficacy of lumbar epidural steroid injections in patients with lumbar disc herniations. Anesth Analg. 2007;104:1217–1222. - PubMed
-
- Manchikanti L. Transforaminal lumbar epidural steroid injections. Pain Physician. 2000;3:374–398. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

