Antihyperglycemic and Antihyperlipidemic Activity of Hydroponic Stevia rebaudiana Aqueous Extract in Hyperglycemia Induced by Immobilization Stress in Rabbits
- PMID: 28758125
- PMCID: PMC5512021
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9251358
Antihyperglycemic and Antihyperlipidemic Activity of Hydroponic Stevia rebaudiana Aqueous Extract in Hyperglycemia Induced by Immobilization Stress in Rabbits
Abstract
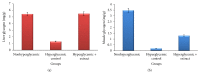
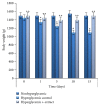
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a serious worldwide problem related to human hyperglycemia. Thus, herbal preparations with antihyperglycemic properties especially leaf extracts of hydroponic Stevia rebaudiana (SR) would be useful in hyperglycemia treatment. The antihyperglycemic potential of this medicinal plant grown using hydroponics methods has been evaluated. Significant reduction of some biochemical characteristics for sugars and fatty acids in blood, liver, and muscle especially fasting glucose levels, serum triglycerides, LDL-cholesterol, total cholesterol levels, and increased HDL-cholesterol ones was shown with SR aqueous extract treatment. Therefore, the aqueous extract of SR is suggested to have antihyperglycemic and antihyperlipidemic activity and to restore liver and muscle glycogen levels (hepatoprotective effects) in hyperglycemia induced by immobilization stress in rabbits and might be recommended for treatment of DM (hyperglycemia).
Figures

References
-
- Berezovskaya I. V., Guskova T. A., Durnev A. D. The methodical recommendations for study of safety reproduced medicinal preparation. Biomedicine. 2011;3:80–86.
-
- Tang J. Z., Mao J. P., Yang Z. F., Zhou Z. G., Tang W. L., Feng Q. Effects of glimepiride and metformin on free fatty acid in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Central South University Medical Sciences. 2004;29:631–634. - PubMed
-
- Martin G. J. Ethnobotany: A “People And Plants”. London, UK: Conservation Manual, Chapman and Hall; 1995.
-
- Haq M. Z., Riaz M., Saad B. Anthocyanins and Human Health, Springer Briefs in Food, Health and Nutrition. Springer International Publishing. 2016:1–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-26456-1_1. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

