Distribution and chemical composition of estrogen receptor β neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the female and male mouse hypothalamus
- PMID: 28758220
- PMCID: PMC5815298
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.24295
Distribution and chemical composition of estrogen receptor β neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the female and male mouse hypothalamus
Abstract
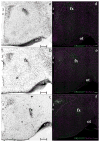
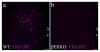
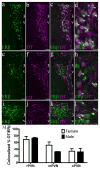
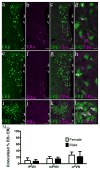
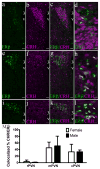
Activation of estrogen receptor beta (ERβ)-expressing neurons regulates the mammalian stress response via the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. These neurons densely populate the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN). Recent research has revealed striking differences between rat and mouse PVN cytochemistry, but careful exploration of PVN ERβ neurons in mice has been hindered by a lack of specific ERβ antisera. Therefore, we used male and female transgenic mice expressing EGFP under the control of the mouse ERβ promoter (ERβ-EGFP) to examine the chemical architecture of PVN ERβ cells. Using immunohistochemistry, we found that 90% of ERβ-immunoreactivity (-ir) colocalized with EGFP. Cellular colocalization of EGFP with neuropeptides, transcription modulators, and neuronal tracers was examined throughout the PVN. ERβ-EGFP cells expressed oxytocin more abundantly in the rostral (71 ± 3%) than caudal (33 ± 8%) PVN. Arginine vasopressin colocalized with EGFP more often in females (18 ± 3%) than males (4 ± 1%). Moreover, estrogen receptor α-ir colocalized with ERβ-EGFP at low levels (15 ± 3%). Using a corticotropin releasing hormone-cre driver X tdTomato reporter mouse, we found a moderate colocalization with ERβ-ir (48 ± 16%) in the middle PVN. Peripheral injection of fluorogold revealed that the rostral PVN ERβ-EGFP cells are neuroendocrine neurons whereas non-neuroendocrine (presumably pre-autonomic) ERβ-EGFP neurons predominated in the posterior PVN. These data demonstrate chemoarchitectural differences in ERβ neurons of the mouse PVN that are different from that previously described for the rat, thus, elucidating potential neuronal pathways involved in the regulation of the HPA axis in mice.
Keywords: ESR2; RRID:IMSR_JAX:007908; RRID:MMRRC_036904-UC; cytochemistry; estrogen receptor beta; paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sex and age influence gonadal steroid hormone receptor distributions relative to estrogen receptor β-containing neurons in the mouse hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus.J Comp Neurol. 2021 Jun;529(9):2283-2310. doi: 10.1002/cne.25093. Epub 2021 Jan 14. J Comp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33341960 Free PMC article.
-
Preautonomic neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus contain estrogen receptor beta.Brain Res. 2003 Jun 13;975(1-2):99-109. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(03)02594-0. Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12763597
-
Differential colocalization of estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) with oxytocin and vasopressin in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the female rat brain: an immunocytochemical study.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Mar 17;95(6):3281-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.3281. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9501254 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the androgen metabolite, 5alpha-androstane-3beta,17beta-diol, in modulating oestrogen receptor beta-mediated regulation of hormonal stress reactivity.J Neuroendocrinol. 2009 Mar;21(4):351-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2009.01840.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19207807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific expression of optically active reporter gene in arginine vasopressin-secreting neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamic-neurohypophyseal system.J Neuroendocrinol. 2008 Jun;20(6):660-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01706.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18601686 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex and interspecies differences in ESR2-expressing cell distributions in mouse and rat brains.Biol Sex Differ. 2023 Dec 18;14(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s13293-023-00574-z. Biol Sex Differ. 2023. PMID: 38111056 Free PMC article.
-
A Common Neuroendocrine Substrate for Diverse General Anesthetics and Sleep.Neuron. 2019 Jun 5;102(5):1053-1065.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.03.033. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 31006556 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic scoping review of the multifaceted role of phoenixin in metabolism: insights from in vitro and in vivo studies.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 27;15:1406531. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1406531. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39398330 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor type 1 (Crhr1) neurons: validating the specificity of a novel transgenic Crhr1-FlpO mouse.Brain Struct Funct. 2024 Dec 18;230(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s00429-024-02879-0. Brain Struct Funct. 2024. PMID: 39692887 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen Receptor Beta Agonist Influences Presynaptic NMDA Receptor Distribution in the Paraventricular Hypothalamic Nucleus Following Hypertension in a Mouse Model of Perimenopause.Biology (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;13(10):819. doi: 10.3390/biology13100819. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alves SE, Lopez V, McEwen BS, Weiland NG. Differential colocalization of estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) with oxytocin and vasopressin in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the female rat brain: an immunocytochemical study. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95(6):3281–3286. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biag J, Huang Y, Gou L, Hintiryan H, Askarinam A, Hahn JD, … Dong HW. Cyto- and chemoarchitecture of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in the C57BL/6J male mouse: a study of immunostaining and multiple fluorescent tract tracing. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 2012;520(1):6–33. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burbach JP, Lopes da Silva S, Cox JJ, Adan RA, Cooney AJ, Tsai MJ, Tsai SY. Repression of estrogen-dependent stimulation of the oxytocin gene by chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor I. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994;269(21):15046–15053. - PubMed
-
- Burgess L, Handa R. Chronic estrogen-induced alterations in adrenocorticotropin and corticosterone secretion, and glucocorticoid receptor-mediated functions in female rats. Endocrinology. 1992;131:1261–1269. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

