Revisiting the Page & Schroeder model: the good, the bad and the unknowns in the periodontal host response 40 years later
- PMID: 28758305
- PMCID: PMC5539911
- DOI: 10.1111/prd.12181
Revisiting the Page & Schroeder model: the good, the bad and the unknowns in the periodontal host response 40 years later
Abstract
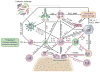
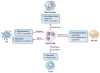
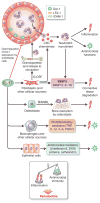
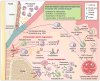
In their classic 1976 paper, Page & Schroeder described the histopathologic events and the types of myeloid cells and lymphocytes involved in the initiation and progression of inflammatory periodontal disease. The staging of periodontal disease pathogenesis as 'initial', 'early', 'established' and 'advanced' lesions productively guided subsequent research in the field and remains fundamentally valid. However, major advances regarding the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the induction, regulation and effector functions of immune and inflammatory responses necessitate a reassessment of their work and its integration with emerging new concepts. We now know that each type of leukocyte is actually represented by functionally distinct subsets with different, or even conflicting, roles in immunity and inflammation. Unexpectedly, neutrophils, traditionally regarded as merely antimicrobial effectors in acute conditions and protagonists of the 'initial' lesion, are currently appreciated for their functional versatility and critical roles in chronic inflammation. Moreover, an entirely new field of study, osteoimmunology, has emerged and sheds light on the impact of immunoinflammatory events on the skeletal system. These developments and the molecular dissection of crosstalk interactions between innate and adaptive leukocytes, as well as between the immune system and local homeostatic mechanisms, offer a more nuanced understanding of the host response in periodontitis, with profound implications for treatment. At the same time, deeper insights have generated new questions, many of which remain unanswered. In this review, 40 years after Page & Schroeder proposed their model, we summarize enduring and emerging advances in periodontal disease pathogenesis.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Abe T, AlSarhan M, Benakanakere MR, Maekawa T, Kinane DF, Cancro MP, Korostoff JM, Hajishengallis G. The B cell-stimulatory cytokines BLyS and APRIL are elevated in human periodontitis and are required for B cell-dependent bone loss in experimental murine periodontitis. J Immunol. 2015;195:1427–1435. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allam JP, Duan Y, Heinemann F, Winter J, Gotz W, Deschner J, Wenghoefer M, Bieber T, Jepsen S, Novak N. IL-23-producing CD68(+) macrophage-like cells predominate within an IL-17-polarized infiltrate in chronic periodontitis lesions. J Clin Periodontol. 2011;38:879–886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

