Intermittent hypoxia training in prediabetes patients: Beneficial effects on glucose homeostasis, hypoxia tolerance and gene expression
- PMID: 28758418
- PMCID: PMC5648288
- DOI: 10.1177/1535370217723578
Intermittent hypoxia training in prediabetes patients: Beneficial effects on glucose homeostasis, hypoxia tolerance and gene expression
Abstract
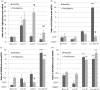
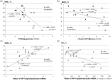
The present study aimed at examining beneficial effects of intermittent hypoxia training (IHT) under prediabetic conditions. We investigate the effects of three-week IHT on blood glucose level, tolerance to acute hypoxia, and leukocyte mRNA expression of hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and its target genes, i.e. insulin receptor, facilitated glucose transporter-solute carrier family-2, and potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily J. Seven healthy and 11 prediabetic men and women (44-70 years of age) were examined before, next day and one month after three-week IHT (3 sessions per week, each session consisting 4 cycles of 5-min 12% O2 and 5-min room air breathing). We found that IHT afforded beneficial effects on glucose homeostasis in patients with prediabetes reducing fasting glucose and during standard oral glucose tolerance test. The most pronounced positive effects were observed at one month after IHT termination. IHT also significantly increased the tolerance to acute hypoxia (i.e. SaO2 level at 20th min of breathing with 12% O2) and improved functional parameters of respiratory and cardiovascular systems. IHT stimulated HIF-1α mRNA expression in blood leukocytes in healthy and prediabetic subjects, but in prediabetes patients the maximum increase was lagged. The greatest changes in mRNA expression of HIF-1α target genes occurred a month after IHT and coincided with the largest decrease in blood glucose levels. The higher expression of HIF-1α was positively associated with higher tolerance to hypoxia and better glucose homeostasis. In conclusion, our results suggest that IHT may be useful for preventing the development of type 2 diabetes. Impact statement The present study investigated the beneficial effects of intermittent hypoxia training (IHT) in humans under prediabetic conditions. We found that three-week moderate IHT induced higher HIF-1α mRNA expressions as well as its target genes, which were positively correlated with higher tolerance to acute hypoxia and better glucose homeostasis in both middle-aged healthy and prediabetic subjects. This small clinical trial has provided new data suggesting a potential utility of IHT for management of prediabetes patients.
Keywords: Intermittent hypoxia; adaptation; diabetes; hyperglycemia; hypoxia inducible factor-1; hypoxia inducible factor-1-regulated genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of intermittent hypoxia training on leukocyte pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK-1) mRNA expression and blood insulin level in prediabetes patients.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019 Mar;119(3):813-823. doi: 10.1007/s00421-019-04072-2. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30701312
-
Intermittent Hypoxia/Hyperoxia Versus Intermittent Hypoxia/Normoxia: Comparative Study in Prediabetes.High Alt Med Biol. 2019 Dec;20(4):383-391. doi: 10.1089/ham.2019.0053. Epub 2019 Oct 7. High Alt Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31589074 Clinical Trial.
-
Acute Hypoxic Test in Patients with Prediabetes.High Alt Med Biol. 2016 Jun;17(2):101-7. doi: 10.1089/ham.2015.0117. Epub 2016 May 23. High Alt Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27213550
-
Multiplicity of hypoxia-inducible transcription factors and their connection to the circadian clock in the zebrafish.Physiol Biochem Zool. 2015 Mar-Apr;88(2):146-57. doi: 10.1086/679751. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Physiol Biochem Zool. 2015. PMID: 25730270 Review.
-
The ability of exercise to meaningfully improve glucose tolerance in people living with prediabetes: A meta-analysis.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020 Feb;30(2):209-216. doi: 10.1111/sms.13567. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020. PMID: 31593613
Cited by
-
Sustained Intermittent Hypoxemia Induces Adiponectin Oligomers Redistribution and a Tissue-Specific Modulation of Adiponectin Receptor in Mice.Front Physiol. 2019 Feb 8;10:68. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00068. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30800074 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy-dependent and -independent modulation of oxidative and organellar stress in the diabetic heart by glucose-lowering drugs.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 May 13;19(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01041-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32404204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controlled Hypoxia Acutely Prevents Physical Inactivity-Induced Peripheral BDNF Decline.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7536. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147536. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062779 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Physiological and Biological Responses to Short-Term Intermittent Hypobaric Hypoxia Exposure: From Sports and Mountain Medicine to New Biomedical Applications.Front Physiol. 2018 Jul 9;9:814. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00814. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30038574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intermittent Hypoxia-Hyperoxia Training Improves Cognitive Function and Decreases Circulating Biomarkers of Alzheimer's Disease in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 30;20(21):5405. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215405. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. Retraction in: Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 07;25(9):5039. doi: 10.3390/ijms25095039. PMID: 31671598 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Xi L, Serebrovskaya TV. Intermittent hypoxia: from molecular mechanisms to clinical applications, 1st ed New York, NY: Nova Science Publishers, Inc., 2009.
-
- Xi L, Serebrovskaya TV. Intermittent hypoxia and human diseases, 1st ed London: Springer, 2012.
-
- Mateika JH, El-Chami M, Shaheen D, Ivers B. Intermittent hypoxia: a low-risk research tool with therapeutic value in humans. J Appl Physiol 2015; 118: 520–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

