Development of a UPLC-MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Six Flavonoids in Rat Plasma after Administration of Maydis stigma Extract and Its Application to a Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study in Normal and Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 28758910
- PMCID: PMC6152039
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22081267
Development of a UPLC-MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Six Flavonoids in Rat Plasma after Administration of Maydis stigma Extract and Its Application to a Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study in Normal and Diabetic Rats
Abstract
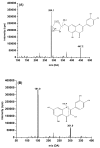
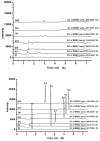
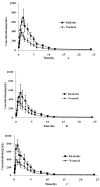
Maydis stigma is an important medicine herb used in many parts of the world for treatment of diabetes mellitus, which main bioactive ingredients are flavonoids. This paper describes for the first time a study on the comparative pharmacokinetics of six active flavonoid ingredients of Maydis stigma in normal and diabetic rats orally administrated with the decoction. Therefore, an efficient and sensitive ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method for the simultaneous determination of six anti-diabetic ingredients (cynaroside, quercetin, luteolin, isorhamnetin, rutin and formononetin) of Maydis stigma in rat plasma has been developed and validated in plasma samples, which showed good linearity over a wide concentration range (r² > 0.99), and gave a lower limit of quantification of 1.0 ng·mL-1 for the analytes. The intra- and interday assay variability was less than 15% for all analytes. The mean extraction recoveries and matrix effect of analytes and IS from rats plasma were all more than 85.0%. The stability results showed the measured concentration for six analytes at three QC levels deviated within 15.0%. The results indicated that significant differences in the pharmacokinetic parameters of the analytes were observed between the two groups of animals, whereby the absorptions of these analytes in the diabetic group were all significantly higher than those in the normal group, which provides an experimental basis for the role of Maydis stigma in anti-diabetic treatment.
Keywords: Maydis stigma; UPLC-MS/MS; anti-diabetic ingredients; pharmacokinetics; rat plasma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Development of an ultra-fast liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous determination of seven flavonoids in rat plasma: Application to a comparative pharmacokinetic investigation of Ginkgo biloba extract and single pure ginkgo flavonoids after oral administration.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017 Aug 15;1060:173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.05.021. Epub 2017 May 30. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28622621
-
Simultaneous determination of four bioactive flavonoids from Polygonum orientale L. in dog plasma by UPLC-ESI-MS/MS and application of the technique to pharmacokinetic studies.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Apr 15;957:96-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.02.055. Epub 2014 Mar 12. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24662144
-
UPLC-MS/MS determination and gender-related pharmacokinetic study of five active ingredients in rat plasma after oral administration of Eucommia cortex extract.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Jul 1;169:145-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.04.007. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25910535
-
Recent developments in stigma maydis polysaccharides: Isolation, structural characteristics, biological activities and industrial application.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 May 1;150:246-252. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.294. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32014475 Review.
-
Corn silk (Stigma maydis) in healthcare: a phytochemical and pharmacological review.Molecules. 2012 Aug 13;17(8):9697-715. doi: 10.3390/molecules17089697. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 22890173 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative pharmacokinetics of four active components on normal and diabetic rats after oral administration of Gandi capsules.RSC Adv. 2018 Feb 9;8(12):6620-6628. doi: 10.1039/c7ra11420f. eCollection 2018 Feb 6. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35540372 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating Polyphenol Nanoformulations for Therapeutic Targets against Diabetes Mellitus.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 21;2022:5649156. doi: 10.1155/2022/5649156. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35832521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous Determination and Pharmacokinetics of Peimine and Peiminine in Beagle Dog Plasma by UPLC-MS/MS after the Oral Administration of Fritillariae ussuriensis Maxim and Fritillariae thunbergii Miq Powder.Molecules. 2018 Jun 28;23(7):1573. doi: 10.3390/molecules23071573. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29958456 Free PMC article.
-
Influence Factors of the Pharmacokinetics of Herbal Resourced Compounds in Clinical Practice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Mar 5;2019:1983780. doi: 10.1155/2019/1983780. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 30949215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of cynaroside on lipid metabolism and lipid-related diseases: a mechanistic overview.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 31;16:1648614. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1648614. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40822468 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ganiyu O., Adedayo O.A., Ayodele J.A., Thomas-Henleb J.A.S., Uwe S. Inhibitory effect of polyphenol-rich extracts of jute leaf (Corchorus olitorius) on key enzyme linked to type 2 diabetes (α-amylase and α-glucosidase) and hypertension (angiotensin I converting) in vitro. J. Funct. Food. 2012;4:450–458.
-
- Diabetes Altas Seventh Edition Committee International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Altas. [(accessed on 7 July 2013)]; Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

